Taxonomic categories can define as the hierarchical classification of the different individuals into a more specific sequence by categorizing them into seven categories starting from the origin to the organisms. The taxonomic category was first given by the scientist Carl Linnaeus in the 18th century. Linnaeus also developed a system called binomial nomenclature.
Linnaean hierarchy, taxonomic hierarchy and taxonomic classification are the alternative terms for the term taxonomic category. It provides a convenient tool to characterize the different organisms based on their observable characters. There are 1.7-1.8 million species in the living world, and remembering each of them is challenging. But, taxonomic categories help us to study the individuals based on their Linnaean classification.
There are seven categories to classify an individual organism. Taxonomic category classifies the organism in a definite descending order by keeping the kingdom’s name first to the following sequence like phylum, class, order, family, genus and species. In this context, we will discuss the definition, important terms and all the seven categories of the taxonomic classification along with the examples.
Content: Taxonomic Categories
Taxonomic Category Definition
The taxonomic category system classifies an individual from the kingdom to a specific division, class, order and family to the more specific categories, i.e. genus and species. It was first given by Carl Linnaeus and also called arrangement law. A particular individual’s arrangement is done based on observable characteristics and identifying features from the increasing order from kingdom to species.
Important Terms in the Taxonomic Category
Taxonomy: Taxonomy can define a term where the different groups of organisms can be classified and arranged into the various taxa.
Taxa: The taxonomy unit comprises different categories to place a particular group of organisms into a particular category.
Example: Taxa of birds is Aves.
Category: A category can define the rank or level of the organism placed in the binomial classification. It includes a hierarchy of seven obligate categories.
Example: The category of bird is Chordata (Organisms possess backbones).
Taxonomic Categories in Order
There are seven taxonomic categories in the Linnaeus hierarchy or classification, which are as follows:
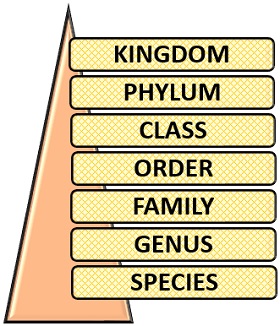
Kingdom
This is the first category of the biological classification. The kingdom is the category of closely related organisms. The kingdom is broadly classified into Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protista and Monera.
Example: All the animals share some common features like a multicellular organization, heterotrophic mode of nutrition, and collagen in the cell wall. Therefore, the animals belong to the kingdom Animalia.
Phylum
It is the second category of the biological classification, which is a group of closely related organisms.
Example: Animals along with the birds, mammals will belong to the same phylum Chordata, as both share a common feature of having a spinal cord.
Class
The class is the third category of the biological classification, which comprises of one or more related order.
Example: Like Mammalia is the class that comprises of related order like:
- Marsupialia (includes kangaroos)
- Cetacean (includes Whale)
- Carnivora (includes lion, tiger etc.)
- Primata (includes apes and human)
All these four orders, i.e. Marsupialia, Cetacean, Carnivora and Primata, share some common features like the presence of mammary gland and hair on the skin.
Order
The order is the fourth category of the biological classification, which comprises of one or more related families. The carnivorous animals have a common feature like small collar bone, strong senses, and strong teeth.
Example: Felidae (a family that includes dog) and Canidae (a family that includes a cat, fox, wolf etc.) are placed in the same order, i.e. Carnivora (by sharing a common feature of having a carnivorous diet).
Family
It is the fifth category of the biological classification. The family comprises a group of the related genus. Here, a term (family) indicates the organisms of the same community those have correlated characters.
Example: The genus of cat is Felis, and the genus of the lion is Panthera, whereas both belong to the same family Felidae due to their hyper carnivorous behaviour.
Genus
The sixth category of the biological classification includes some closely related species that show some similarities among the species of the same genus but differs from the other genus.
Example: Mucor is the genus comprising multiple species that will somehow relate to each other but differ from the other genus like Rhizopus.
Species
It is the last category of the biological classification. Species are highly diversified in nature. One species can be differentiated from the other by observing differences in morphology and chemical and physical properties. Therefore, each species will show some distinctive feature that will discriminate one species from the other.
Example: Bacillus is a genus that comprises species like Bacillus subtilis, and Bacillus anthracis, which cause different effects on the body.
It helped a lot in making my notes. Thank you for this information!
Thank you!