Vermicomposting is a composting technique, which turns the organic debris into a humus-like product by employing earthworms. “Vermicompost” is the compost produced by the vermicomposting unit.
The vermicompost merely refers to the earthworm’s excrement, which provides essential nutrients, aeration, porosity, structure, fertility and water-holding capacity to the soil and plant body.
The vermicomposting method requires an average temperature between 15-25 degrees Celsius, tropical climate and green wastes. It prevalently uses Eisenia fetida to degrade the organic green wastes due to their best appetites and breeding ability.
This post discusses the definition, purpose, requirements, mechanism, vermicomposting process, and the advantages and disadvantages. You would also get to know the meaning of vermicompost and the preparation of worm tea.
Content: Vermicomposting
- Meaning
- Purpose
- Vermicompost
- Requirements
- Mechanism of digestion
- Process
- Advantages and Uses
- Disadvantages
- Worm Tea
Vermicomposting Meaning
Vermicomposting refers to the aerobic process that aids earthworms to produce organic compost through animal and plant waste decomposition. “Vermicompost” is the product of the vermicomposting unit.
Worms digest the agro, plant and farm wastes by the grinding action of their gizzard, and they excrete granular casts or “Vermicasts”. The earthworm castings contain simpler nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, etc., which the plants can directly use up.
Purpose
The vermicomposting method aims at the following objectives:
- Production of quality compost.
- Participates in waste recycling and solid-waste management by recycling the agro and farm waste into useful bioorganic manure.
- Increases crop yield by improving soil fertility.
- Promotes the organic farming system.
- Augmentation of food production.
- Allocates employment opportunities to the members of a rural family.
Vermicompost Meaning
Compost is a product obtained from the microbial decomposition of organic wastes. In contrast, vermicompost or vermicasting refers to the useful, granular castings excreted by the complete pulverization of agro and farm wastes by the earthworms.
Vermiculture requires nearly 1000-1200 worms to decompose 1kg/q of organic matter. Vermicompost provides nutrient and humus-rich soil that conditions the soil and nourishes the plant’s growth. It serves as the organic fertilizer for crop yield and development.
Requirements of Vermicomposting Procedure
The process of vermiculture requires feedstock or raw materials like plant and animal excreta and earthworms to break down the organic matter into simpler minerals and nutrients. In addition to this, it also requires water to maintain 40% of the minimum moisture content.

Raw materials
It includes organic green wastes like waste coming from farms, kitchen, forest etc. The ratio of waste and dung should be 1:1. Raw materials act as feedstock for the earthworms, which should have the following ideal properties:
- It should contain 75% of water content.
- The density should be below 640lb/ft3.
- It should be devoid of any chemical, pesticide and tannins residues.
Earthworms
They can be epigeic, endogeic and anecic in habitat. Eisenia fetida is a red wiggler, mostly preferred over the other types. They can decompose and convert the organic matter into vermicompost within 45-50 days or have a high metabolic rate. Eisenia fetida is the most common species of earthworm used throughout the world to perform the vermiculture technique.

Mechanism of digestion
Firstly, the earthworms take up the organic debris like plant and animal wastes into their gut. Then, the organic wastes pass from the earthworm’s gut and mineralize into ammonium and later into the plant’s minerals and nutrients.
The grinding action of the gizzard and the chemicals of the digestive tract help in converting the organic debris into the simpler plant’s nutrients. A movement of gut muscle helps in releasing granular vermicasts (rich in the nutrient source).
Vermicomposting Process
The method of vermiculture involves the collection of earthworms, construction of compost pit or bed, harvesting of compost, packaging, and marketing.
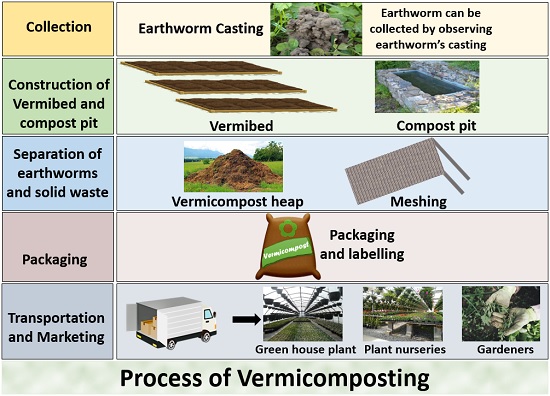
Collection of Earthworms
It includes the following steps:
- Firstly, observe the earthworm castings over the soil surface.
- Then, make a solution containing 500 g of jaggery, 500 g of cow dung and 2 l of water.
- After that, sprinkle the above solution over the soil surface about an area of 1m X 1m.
- Cover with straw lumps, then with the old jute bag, and keep sprinkling the solution for about 20-30 days.
- Finally, we can collect the earthworms after their aggregation towards the spot.
Construction of Vermicomposting Unit
Vermiculture is a method of producing vermicompost, which can be achieved by constructing either a compost pit or a compost bed.
Compost Pit
It can be constructed in a backyard or field and usually carried out in a cemented pit. The recommended size of the pit is 5X5X3 feet, which may vary relative to the volume of biomass and agricultural waste. The ditch is generally covered with the thatched grasses, dry leaves, twigs etc.
Compost pit is usually a non-preferred method because it has aeration and drainage problems. To prevent the entry of ants from attacking the earthworms, the water column should be in the centre of the parapet wall of the compost pit.
Vermibed or Compost Bed
It is recommended over the method of vermiculturing through compost pit. To construct vermibed, we need to follow the given steps:
- Step-1: Prepare the first layer by adding loamy soil at the bottom of thickness about 15-20 cm.
- Step-2: Prepare a second layer by adding broken sticks, pebbles, coarse sand of thickness about 5 cm.
- Step-3: It is the most crucial step that involves the addition of earthworms. Around 150 worms are added to the 2m X 1M X 0.75M compost bed with a thickness of 15-20 cm.
- Step-4: Prepare the fourth layer by addressing some animal wastes like cow dung, goat dung etc. Over this, add a layer of agro-wastes like dry leaves, wheat straws etc., up to a thickness of 5 cm.
- Step-5: Continuous watering is needed for the next 30 days after the construction of vermibed. We need to keep in mind that the feed must not be dry or soggy during this step.
- Step-6: Afterwards, cover the vermibed with either coconut leaves or old gunny bags instead of plastic to avoid the heat trapment. This step prevents birds attack.
- Step-7: Finally, spread the pre-digested organic debris up to the thickness of 5 cm, and repeat this step twice a week.
After all these steps, turn over the organic debris via pickaxe or spade and allow regular watering. The production of humus-rich, granular and dark black coloured vermicompost usually takes 2-3 months.
Harvesting of Vermicompost
The vermicompost is ready for harvesting after the earthworm’s excrements or castings are observable over the soil surface. During this stage, you need to separate the worms and solid wastes manually. To separate the earthworm and solid waste, stop watering for 2-3 days so that the earthworms move towards the bottom of the bed.
Then, subject the compost to the light treatment, after which the earthworms will migrate towards the cooler base. At last, eliminate the worms and the solid wastes using sieves or meshes.
Quality Checking and Packaging
At the time of quality checking, the soil texture, colour, porosity, odour, moisture etc., are the parameters taken into consideration. The vermicompost should have granular texture, dark-black coloured, lightweight, earth-like smell and 40% moisture content.
A musty smell from the compost indicates mould or any lousy odour indicates incomplete decomposition.
While packaging, sieve the vermicompost to ensure the elimination of any plant and animal remnants. Then, transfer the vermicompost into the laminated over sacs to avoid moisture loss and label it with the brand’s name, nutritive facts, direction for use, market price etc.
Finally, it is ready for marketing, which targets the people engaged in nurseries, farming, landscapers, gardeners etc.
Advantages and Uses of Vermicomposting
Vermicomposting is an Eco-biotechnological method having diverse benefits and applications in the following fields:
Soil Physiology
- Vermicompost improves the soil quality, soil structure and texture by providing a humus-rich environment.
- It also nourishes and conditions the soil by increasing the soil’s water-holding capacity and aeration.
- Vermicompost prevents the soil from drought and soil erosion.
- Unlike chemical fertilizers, it does not harm the soil microbiota.
Plant Physiology
- Vermicompost promotes the excellent growth of plants by providing essential nutrients.
- It also helps in the seed germination and yield of the plant.
Food and Crop Improvement
- Vermicompost minimizes the prevalence of crop diseases by the different agents like pests, bacteria, mould etc.
- It promotes healthy living by producing bio-organic food free of chemicals.
Ecological Importance
- Vermicompost reduces land pollution by converting bio-waste into plant’s usable materials from being discharged into landfills.
- It curtails the emission of greenhouse gases (methane, nitric oxide, etc.) produced from landfills.
- It also reduces the demand for chemical fertilizers.
Economical Importance
- Vermicompost acts as a medium, providing a supplemental source of income by employing individuals in rural areas.
- It requires low capital investment and simple technologies.
Disadvantages of Vermicomposting
Vermicomposting has few limitations:
- It requires more labour-power and skills for the operation and maintenance of vermicompost.
- The vermicomposting method also needs more space for the construction, harvesting and storage of vermicompost.
- Environmental factors like temperature, direct sunlight, drought may affect the process.
Worm Tea
It refers to the vermicompost tea or a liquid extract obtained from the vermicompost. To prepare worm tea, take any old t-shirt, muslin cloth or tea bag filled with vermicompost.
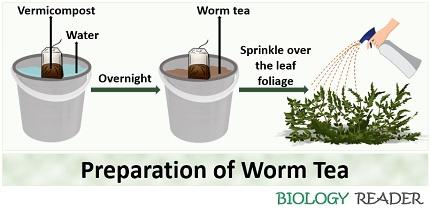
Then, dip the bag into the bucket containing water for overnight. Then, you will obtain a light brown coloured solution that you need to transfer into the spray bottles. Spraying the worm tea solution to the plant foliage suppresses the transmission of plant diseases.