Hydroponic systems cultivate plants in nutrient-rich water with or without using non-soil growing media around the root system. It includes deep water culture, wick system, Ebb and flow, nutrient film technique, drip system and aeroponics.
For the commercial production of plants through hydroponics, a greenhouse is recommended best to cultivate plants like tomatoes, peppers, lettuces, watercress, celery, cannabis and some herbs.
The reason why hydroponics is popular nowadays is because of its less consumption of resources. Plant in the soil-based medium consumes more water than the plants in the hydroponic systems.
Hydroponic systems provide a closed environment for plant growth, which ensures low evaporation of water than in the soil.
The hydroponic systems are entirely recyclable, in which we can filter and refill the water with essential nutrients.
Thus, the water is constantly recycled instead of wasted. This post discusses the meaning, key points and methods of hydroponics.
Content: Types of Hydroponics Systems
Meaning of Hydroponic Systems
Hydroponics is soilless farming that ensures plant cultivation without soil. It enables a faster growth rate and high yield of plants in nutrient-rich water than the plants grow in the soil. For this reason, hydroponics farming has gained wide acceptance in the agriculture field. Yet, the hydroponics system has been known since ancient times.
Examples:
- The ancient city of Babylon, with its famous hanging gardens.
- Floating gardens of the Aztecs of Central America.
The above two are the known examples that prove hydroponics as a traditional method of growing plants in water.
Key Points
- The hydroponic system allows plants to retrieve nutrients directly.
- Hydroponics are water-based systems containing all the essential nutrients necessary for plant growth.
- It uses non-soil growing media like perlite, peat moss, clay pellets etc., to support plants standing upright.
- Plant roots directly retrieve nutrients, water and a sustainable amount of oxygen necessary for their growth.
Six Types of Hydroponic Systems
The below six methods differ in how the systems deliver water, nutrients and oxygen to plant roots.
- Deepwater culture
- Wick system
- Ebb and flow
- Nutrient film technique
- Drip system
- Aeroponics
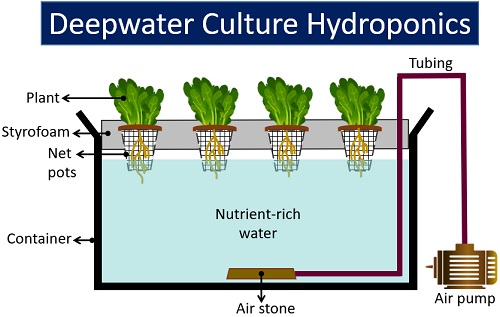
Deepwater Culture Hydroponics
It is also called a reservoir system. The reservoir in DWC contains water and nutrient solution. Here, the plant roots are in direct contact with the nutrient source.
It means there is no support material between the plants and nutrient sources. A diffuser or air stone allows uniform distribution of oxygen in the reservoir.
Thus, plant roots submerged in the reservoir directly absorb nutrients, water and oxygen. The deepwater culture system uses net pots to keep plants in their proper position.
Advantages
- It is a simple method for the operation.
- DWC is an inexpensive method for most growers, requiring a reservoir, suspension system and air pumps.
- Plants in DWC grow faster as they have direct access to nutrients, water and oxygen. Large size plants with big root systems can proliferate through this method.
- You can top up the nutrient solution.
- DWC method produces less waste, as it is a recirculating process.
Disadvantages
- The maintenance of DWC is not easy, as you can only clean the system when it’s not in function.
- Several root diseases may occur in case of dirty growing conditions and stagnant nutrient solutions.
- Here, the basic air pumps do not provide good aeration, or there is no uniform oxygen distribution to all the plants.
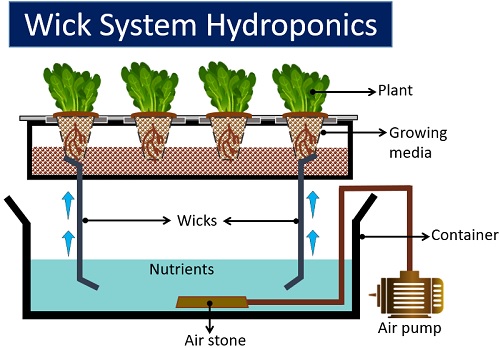
Wick Hydroponic System
It is the simplest type of hydroponics. The Wick system works without the use of aerators or pumps. The plant is fixed within the porous absorbent media (like perlite or coconut coir).
Wick hydroponic systems use a nylon thread to supply water and nutrients to the plants. Here, one end of nylon thread is around the absorbent media and the other end is immersed in the reservoir.
The Wick system is best for plants that consume very less water and nutrients to grow. The wick or nylon thread supplies water and nutrients whenever the roots are ready to absorb.
It is a passive system because there is no involvement of electricity, air or water pumps.
Advantages
- The Wick system is best for growing smaller plants like herbs.
- It is simple to operate as the wick system does not need equipment like a pump and aerators.
- Wick hydroponics is an inexpensive method.
Disadvantages
- The Wick system is only useful in cultivating plants that do not need an adequate water supply.
- It is not suitable for growing heavy-feeding plants, as they need more nutrients to grow.
- There is an uneven distribution of water and nutrient in this system.
- For the maintenance, you need to flush extra nutrients with fresh water every 1-2 weeks.
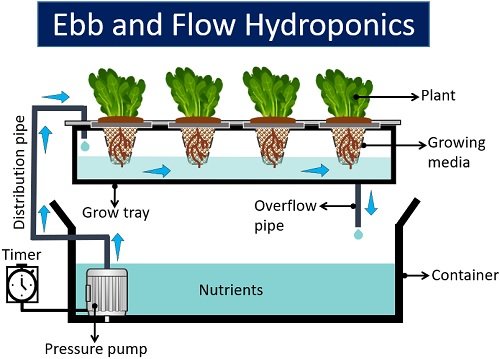
Ebb and Flow Hydroponic System
It is common for home gardening and is also termed the flood and drain system. Here, a growing material like Rockwool or perlite houses the plants.
Then, a growing material holding the plant is positioned within the cavities of a grow bed or grow tank. In this system, the water pump distributes a nutrient-rich solution into a grow bed until the water level reaches a certain height from the bottom of the reservoir to the top layer of the growing medium.
The water pump is outfitted with a timer that regulates the flow of nutrient-rich water. The water pump floods the nutrient solution in the grow tank on a cyclic schedule. After a predetermined time, the timer shuts off the water pump.
As a result, the water drains out from the grow bed and returns to the reservoir. The air pump in the Ebb and Flow system oxygenates the water in the reservoir.
Advantages
- The Ebb and flow method is suitable for growing root vegetables like carrots and radishes.
- It is a recirculating system that effectively uses water and energy.
- Knowing the plant growth intake of nutrients, the Ebb and flow method work best. We can improve the plant’s growth and yield by providing limited nutrients.
Disadvantages
- The method is not successful for growing large plants.
- Its operation requires continuous monitoring of the factors like water and pH.
- The flood and drain methods do not fulfil the nutrient requirements of the plant roots.
- The pump controller can malfunction.
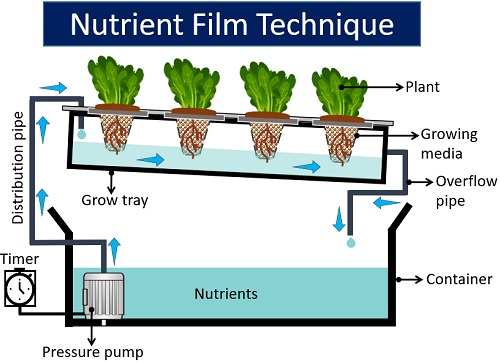
Nutrient Film Technique
It is a simple method for commercial and home gardens. The reservoir of the nutrient film technique contains nutrient-rich water and a motor.
The water pump drives the nutrient-rich solution upwards to the sloping channel. Here, the grow tray appears as a sloping channel. The plants are put inside the net pots with or without the growing media.
When the pressure rises, the motor push water to the grow tray for a predetermined time. Once the time is over, the motor switches off, and the excess nutrient solution gets back into the reservoir.
Advantages
- It is a low-waste recirculating technique.
- To support the plant material, you do not need growing media.
Disadvantages
- Overgrowth of roots may occur that sometimes intertwine along the channel.
- Malfunction in the motor may occur after continuous operation.
- Recirculation of nutrient solutions can clog pipes and channels.
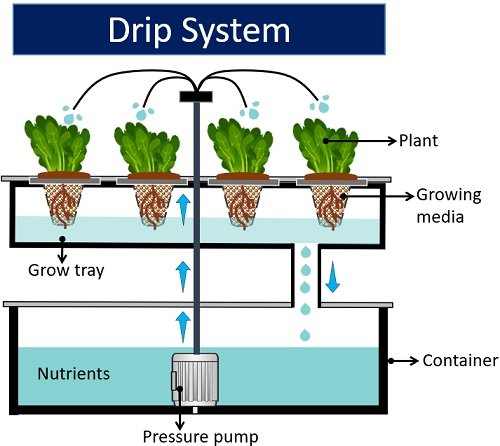
Drip Hydroponic Systems
These are common in commercial settings. Like NFT systems, there is a separate channel holding up the plants. The plants are suspended in net pots over a thin layer of water and nutrient solution.
A large tube pumps the water over the growing channel at a constant rate. This improves oxygenation and nutrient uptake by the plants. The leftover solution flows back into the reservoir.
Drip systems can be circulating or non-circulating systems. Circulating systems drip rapidly with excess nutrients flowing back into the reservoir. Non-circulating systems drizzle slowly with adequate nutrients at a consistent rate.
Advantages
- Drip systems are easy to use and set up.
- It is an efficient technique for growing all types of plants.
- Drip systems efficiently control the schedule of feeding.
- For commercial spaces, it is an inexpensive and effective method.
Disadvantages
- Drip systems need many moving parts that increase the cost for home gardeners.
- It requires continuous tracking of the pH and nutrient level to operate the drip system.
- A drip system is not a recirculation method, leading to a high waste level.
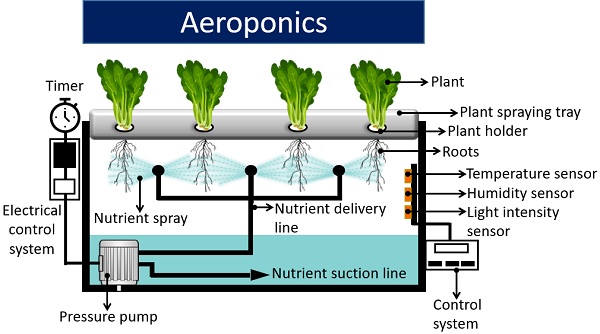
Aeroponics
It is the easiest type of hydroponic system. Here, plants and their roots are suspended in the air. The water pump in the reservoir comprises several mist nozzles.
Misters give a fine spray of the nutrient solution onto the roots of each plant. The rest of the nutrient solution falls into the reservoir.
To construct aeroponics, you must have an idea of the correct dimensions of the reservoir. For instance, a reservoir should be deep to grow larger plants. Plants in the aeroponic system get enough oxygen as they are suspended in the air.
Advantages
- Roots are exposed to more oxygen.
- The operation and maintenance of aeroponics are quite easy.
Disadvantages
- The system is a cost-effective and high-tech method to construct.
- The nozzle in the aeroponics system sometimes becomes clogged, which requires frequent cleaning.
Conclusion
We have always heard that plants need soil, water, and sunlight to grow. But what if that wasn’t true? It’s possible to produce a plant without soil using hydroponics technology.
Instead of soil, we can use organic coco coir and rock wool to support the root system. The nutrient-rich water allows the efficient growth of plants, as the root system is in direct contact with the nutrient source.
Thus, we can conclude that the hydroponic systems force-fed the plants by supplying all the nutrients they needed to sprout into flourishing specimens.
Thanks for explaining how hydroponics involves plant cultivation in the absence of soil by providing plants with nutrient-rich water that helps them grow. I imagine if you do hydroponics farming for a living, it would be best to have the supplies for it from a trusted distributor and provider.