A laminar airflow chamber refers to an enclosed cabinet, which is equipped with a HEPA (high-efficiency particulate air) filtered airflow system. It provides an aseptic environment to perform different experiments.
Laminar airflow cabinet circulates unidirectional airflow with little or no turbulence at a uniform velocity between 0.3-0.5 m/s. It is extensively used in laboratories to maintain the aseptic or contaminant-free working atmosphere.
In this context, we will discuss the definition, principle, uses and horizontal and vertical types of the laminar airflow chamber using well-labelled diagrams. Also, the parts and function of the Laminar airflow cabinet are explained with a diagram.
Content: Laminar Airflow Chamber
Definition of Laminar Airflow
Laminar airflow refers to the airflow system in which the filtered air through the HEPA filter moves within a definite space at uniform velocity and direction.

Running procedure: To run the laminar airflow, you need to wipe the laminar airflow chamber. After that, you need to surface sterilize the workstation by closing the glass shield and switching on the UV light for 15 minutes.
Then, switch on the blower for 5 minutes before the operation. After that, open the sash and also turn on the fluorescent light to perform the desired experiment. After performing the experiment, close the sash or glass shield.
Laminar Airflow Chamber Principle
The working of laminar airflow depends on the high-efficiency particulate airflow system, eliminating all the air-borne contaminants to maintain a sterile environment. So, it is important in microbiological studies or experiments, as it provides an aseptic workstation.
Besides, high-efficiency particulate air filter, two more elements, such as filter pad and fan, are also crucial for the working of the laminar airflow chamber. Fan or blower sucks the prefiltered air from the filter pad that primarily traps the air contaminants.
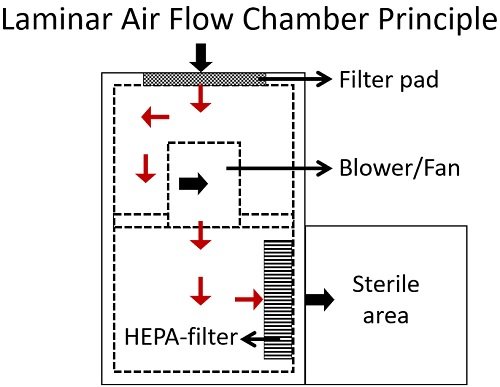
Then, the prefiltered air goes through the high-efficiency particulate air filter that removes the contaminants like fungal spores, bacteria, dust etc. As a result, sterile air flows within the working area at a uniform speed and direction.
Video: Laminar Airflow Chamber
Parts of Laminar Flow Chamber
Enclosed cabinet system: It is made up of stainless steel. Cabinet provides an enclosed system of insulated air throughout the workstation. Thus, it protects the inner sterile air from the outside environment. The front of the cabinet has a glass shield or sash, which function as a sliding front door. Users can open the front door manually and adjust its opening height as needed.
Working platform: It provides a space to perform different experiments or operations. It is also made of stainless steel. We can keep the culture plates, blower, biological samples, and desired materials inside it.
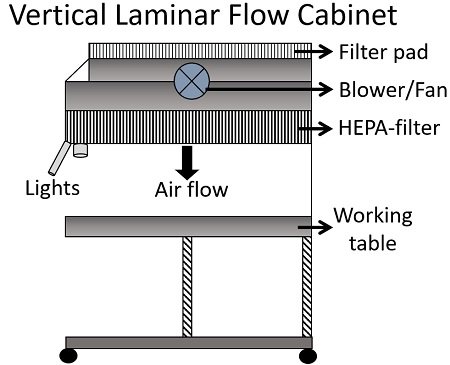
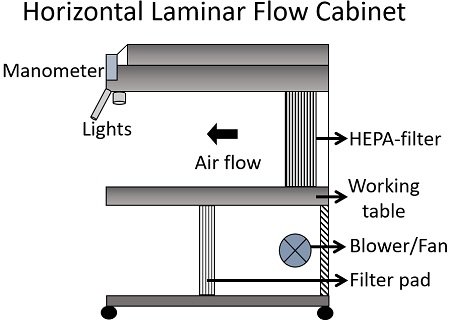
Filter pad: It refers to the prefilter or primary filter that primarily sucks the room air. A filter pad is surmounted at the top of a vertical laminar flow cabinet and at the bottom of a horizontal laminar flow cabinet. It traps the particulates from the room air of size 5 microns or higher.
Blower or Fan: It draws the prefiltered air from the filter pad and throws it towards the high-efficiency particulate air filter. In the vertical laminar flow cabinet, the blower is present below the filter pad. Conversely, the blower is present right next to the filter pad in the horizontal laminar flow cabinet.
Hepa filter: It is a secondary or final filter that offers 99.9% efficiency to eliminate 0.3-micron particulates. Hepa filter is present within the chamber that ensures sterile conditions for the operations or experiments to be taken place.
UV germicidal lamp: It sterilizes the chamber, as well as the contents like Petri plates, test tubes, culture media etc., before the experiment. The user needs to turn on the UV lamp for at least 15 minutes before the operation.
Fluorescent lamp: It provides proper light during the operation.
Hepa Filter in Laminar Airflow
Hepa filter removes particulates or aerosols, not vapours or gases. It traps the particles based on either of the three mechanisms.
- Interception: Particles adhere around the filter fibres.
- Impaction: Sudden changes in the airflow, the particles run into the filter fibres and become embedded.
- Diffusion: Particles interact with surrounding molecules and show Brownian movement. The microorganisms and other particulate matter trapped within the filter fibres moves in a zig-zag manner.
Hepa filter captures the large particles through interception and impaction, whereas it captures small particles via diffusion.
Types
Vertical displacement airflow chamber: It is extensively used in labs. Here, the room air goes to the HEPA filter vertically from the prefilter through the blower or fan in between. Air flows downward from the top of the laminar airflow.
The vertical laminar cabinet does not need more workspace. In addition, its operation is much safer than the horizontal laminar cabinet, as the air does not blow directly towards the user handling the operation.
Horizontal airflow chamber: Here, the room air enters the HEPA filter placed on the back of the cabinet. Air flows horizontally from the back of the laminar airflow.
In the horizontal laminar cabinet, the air moves parallel to the workspace and sterilizes the workstation with a steady airflow. The effluent air directly hits the user.
Uses of Laminar Airflow
- It is ideal for performing plating methods of the prepared culture media.
- We can also perform tissue culture in the horizontal laminar airflow.
- The vertical laminar airflow provides the best workplace to perform different operations related to hazardous specimens.
- It is also ideal for preventing contamination of the particle sensitive materials, semiconductor wafers.
- We can perform the culturing of the biological specimens.
- It provides a favourable environment to perform different operations in the medical, pharmaceutical, electronic and industrial sectors.
Precautions
You need to turn on the UV light before and after the experiment. Never use the blower and UV lamp at the same time. You need to surface sterilize the workspace and sash before and after the experiment by using ethyl alcohol. The user should wear a mask, gloves and lab coat while performing the experiment.