ABO blood grouping is based on the principle of an agglutination reaction. It is the popular method for blood group identification to determine the presence and absence of cellular antigens and their relative antibodies in the blood. In blood typing, the detection of antigen in the donor’s RBCs is called forward typing. In contrast, the detection of antibodies in the donor’s plasma or serum is known as reverse typing.
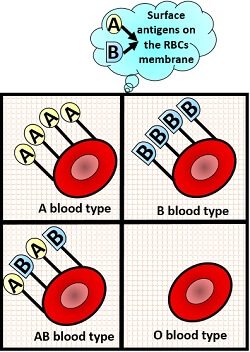
According to the ABO-blood group system, A, B, AB and O are the four phenotypes. Type A and B are the two antigens associated with the RBC membrane, while anti-A and anti-B are the two antibodies naturally present in the blood plasma. The blood typing or the blood group identification is performed by the blood-test kit that contains anti-A, anti-B and anti-D antisera.
The antigens of the ABO blood group system are glycolipid in nature, and the antibodies are predominantly of IgM type. In this context, we will study the principle, method and result interpretation of the ABO blood typing. Besides, we will also discuss some of the discoveries, facts and the overview of the ABO blood group system.
Content: ABO Blood Group System
Meaning of ABO Blood Group System
The ABO blood group system has type A, B, AB and O phenotypes and it is used to identify the type of surface antigens and antibodies present in the donor’s blood. If agglutination occurs in the RBCs, then the corresponding antibody must be absent in the blood plasma. The antigens if absent on the RBCs membrane, then the corresponding antibodies must be present in the blood plasma. Individuals above 3-6 month have naturally occurring antibodies which arise without any antigenic stimulation from the maternal placenta. These antibodies belong to the IgM class. ABO blood group is also present in some other animals like gorillas, chimpanzees etc.
Principle
In the ABO blood grouping system, agglutination reaction takes place between the surface proteins that are found on the red blood cell surface. This surface protein called antigen or agglutinogen. The antigens are mainly glycolipids which are of two types, namely self-antigens and foreign-antigens.
If the antigen is foreign, it will induce the immune response, after which the WBCs come into action to recognize these antigens. Then the WBCs starts making antibodies against that particular antigen. Antibodies are the molecules that work against the antigen and also called agglutinins that float in the blood plasma.
History of ABO Blood Grouping
| Year of discovery | Discoverer | Discovery |
|---|---|---|
| 1900 | Karl Landsteiner | Discovered the ABO blood group system |
| 1901 | Karl Landsteiner | Classify human blood into A, B & C group based on agglutination reaction |
| 1907 | Jan Jansky | Classify blood type O, A, B & AB in roman letters I, II, III & IV |
| 1907 | Reuben Ottenberg | Introduces blood typing in transfusion |
| 1910 | Ludwik Hirszfeld and Emil Freihers Von Dungern | Described genetic inheritance of blood group |
| 1914-15 | Blood clot prevention technique was introduced during first world war by citric acid | |
| 1924 | Felix Bernstein | Introduced the blood group inheritance pattern for multiple alleles |
| 1927 | Karl Landsteiner | ABO blood group system was accepted by National Research Council |
| 1930 | Karl Landsteiner | Awarded by Nobel prize in physiology and medicine |
| 1950 | ABO blood group system was universally followed | |
| 1978 | Finne | Described the presence of polylactosamine chains in the human erythrocyte glycoproteins |
Overview
According to the ABO blood group system, there are four blood groups, namely A, B, AB and O.
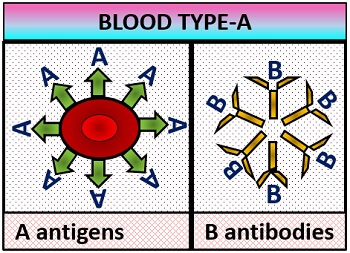
- A–blood group: It possesses A-surface antigens are present on the RBC membrane, and the antibodies in the blood plasma are anti-B type.
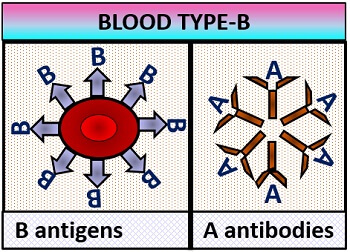
- B–blood group: It possesses B-surface antigens are present on the RBC membrane, and the antibodies in the blood plasma are anti-A type.
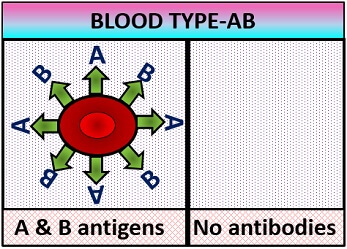
- AB–blood group: It possesses surface antigens on the RBC membrane that are A and B antigens and no antibodies in the blood plasma.
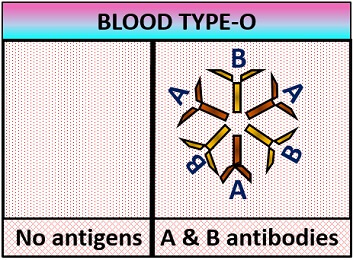
- O–blood group: It has no surface antigens present on the RBC membrane, and the antibodies in the blood plasma are of both anti–A and anti–B type.
Method of ABO Blood Group System
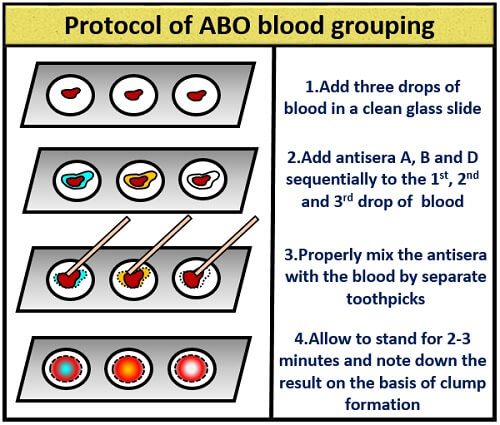
ABO blood group method can be performed by the “Slide technique” which includes the following steps:
- First, scrub the middle finger with cotton saturated with 70% of alcohol.
- Then, prick the middle finger by sterilized needle or lancet.
- After that, place three drops on a clean glass slide.
- Then after this, add antisera in a sequence of anti- A in a first drop, anti- B in a second drop and anti- D to the third drop, respectively.
- Mix the blood with the antisera separately by using a sterilized toothpick.
- Allow the slide to stand for 2-3 minutes and then note down the results based on clump formation or agglutination reaction.
Interpretation of Result
The results on the ABO blood group system are based on agglutination reaction.
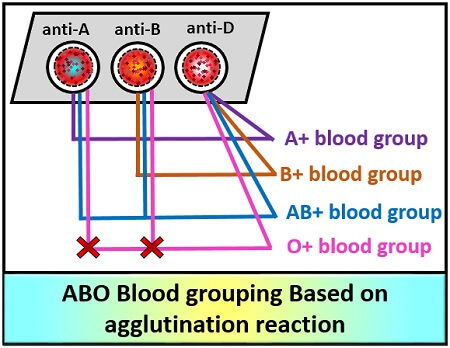
- If the agglutination occurs in the RBCs, to which anti-A is added, then the blood group is ‘A’.
- When agglutination occurs in the RBCs, to which anti-B is added, then the blood group is ‘B’.
- If the agglutination occurs in the RBCs, to which both anti-A and B are added, then the blood group is ‘AB’.
- When there is no agglutination occurs in the RBCs, then the blood group is ‘O’.
In addition, there is also another antiserum that is anti-D, which determines the positive and negative blood type.
- If the agglutination occurs in the RBCs to which anti-D is added, then the blood type is positive (+) and if no agglutination occurs in the RBCs mixed anti-D, then the blood type is negative (-).
ABO Compatibility
Theory of blood transfusion states that before transfusion, the ABO compatibility of blood type must be checked, as any carelessness can affect the immune system.
- A person with blood group A can receive blood from the person with blood types A and O.
- The person with blood group B can receive blood from the person with blood types B and O.
- A person with blood group AB can receive blood from the person with all blood types A, B, AB and O and called as Universal recipient.
- The person with blood group O can receive blood from only the person with blood type O.
| Recipient blood type | Can take blood from the person with blood type |
|---|---|
| A | A and O |
| B | B and O |
| AB | A, B, AB and O |
| O | O |
- A person with blood group A can donate blood to the person with blood types A and AB.
- The person with blood group B can donate blood to the person with blood types B and AB.
- A person with blood group AB can donate blood to only the person with blood type AB.
- A person with blood group O can donate blood to the person with all blood types A, B, AB and O and hence called Universal donor.
| Donor blood type | Can give blood to the person with blood type |
|---|---|
| A | A and AB |
| B | B and AB |
| AB | AB |
| O | A, B, AB and O |
Conclusion
Therefore, the ABO blood group system is one of the popular technique to classify human blood. ABO blood group system majorly classifies the blood into four types, i.e. A, B, AB and O. Agglutination reaction determines the ABO blood type, which is determined by the clump formation in the blood. ABO blood group system was accepted by the National Research Council and popularly known as Landsteiner classification. Karl Landsteiner won the Nobel prize in the year 1930 for his contribution in this.