Difference between absorbent and adsorbent is mainly due to the following factors like their mechanism and the phenomena they follow:
Mechanism: The mechanism of absorbent and absorbent is to retain the particles or molecules, in which a former absorbs the particles into the matrix, and the latter adsorbs the particles over the solid matrix.
Phenomena: Absorption and adsorption are the phenomena, which makes the use of absorbent and adsorbate, respectively. Both the processes differ in principle, by what mechanism they allow the particles to enter.
Content: Absorbent Vs Adsorbent
Comparison Chart
| Properties | Absorbent | Adsorbent |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | The absorbent is a kind of matrix, which allows the solid, liquid and gaseous particles into the surface of the matrix | The adsorbent matrix can define as a matrix, which retains the particles of the liquid and gaseous medium over the surface of the matrix |
| Particle separation | The absorbent media absorbs the absorbate particles that are capable of being absorbed into the media | The adsorbent matrix adsorbs the particles termed as adsorbate that are capable of being adsorbed over the surface matrix |
| Working | Absorbent works by a principle of dissolution, diffusion or osmosis, which allows the specific particles to enter into the matrix | Adsorbent works by a principle of adhesion, which allows the particles to adhere over the surface of the matrix |
| Phenomena | It works by phenomena of absorption | It works by phenomena of adsorption |
| Heat exchange | The interaction forces between the absorbent matrix and the absorbate molecules exhibit an endothermic heat energy | The interaction forces between the adsorbent matrix and the adsorbate molecules exert an exothermic energy |
| Effect of temperature | The temperature has no effect on the process of absorption | Adsorption is a temperature- dependent process |
| Particle separation | Particles absorbs within the absorbent matrix | Separates particle over the adsorbent matrix |
| Interaction between the particles and the matrix | The absorbed materials get into the absorbent through different phases of matter or some chemical reaction | The adsorbed materials stick to the adsorbent via Van der Wall’s forces or covalent bond interaction |
| Examples | Cotton wool, paper towels etc. | Activated alumina, silica gel, activated charcoal, clay etc. |
Definition of Absorbent
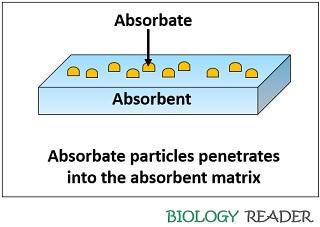
The absorbent can define as a material which absorbs the particles or allow the particles to enter through its surface, and the process is commonly termed as absorption. The particles that are absorbed by the absorbent matrix are said to be absorbate materials.
Through the process of absorption, many solid, liquid and gaseous particles may enter into the absorbent either via dissolution, diffusion or osmosis. Therefore, absorbent requires physical energy from outside to separate the particles within the matrix.
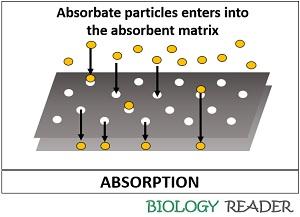
The process of absorption can be understood by taking an example of an absorbate as juice and absorbent as tissue paper. Tissue paper immediately absorbs the liquid substance, so the juice will get absorbed within the pores of a tissue paper that it becomes unidentifiable to separate that.
Here, the interaction between the absorbent and absorbate particles is persistent but does not involve any kind of physical or chemical interaction. The rate of absorption is uniform, and the heat exchange between the surface and surrounding is endothermic, i.e. requires energy from outside.
Types
Chemical absorption: It is a chemically reactive process, which occurs between the absorbate particles and absorbent matrix. For example, aqueous sodium hydroxide (an absorbent) dissolves an acid gas.
Physical absorption: It is chemically non-reactive and the process occurs between two phases of matter. For an instance a liquid absorbs a gas like in the water, there is a certain amount of dissolved oxygen. It depends on the phases and the physical properties of absorbate like solubility and other factors like pressure and temperature.
Definition of Adsorbent
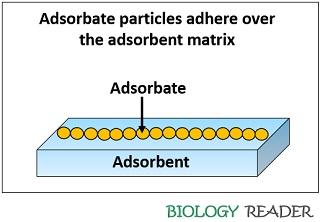
The adsorbent can define as a matrix which separates or retain the particles over its surface, through the phenomena commonly termed as adsorption. The particles that are separated by the adsorbent matrix are said to be adsorbate materials.
Through the process of adsorption, many dissolved solid, liquid and gaseous particles can get separated over the surface of the absorbent via adhesion of particles. Therefore, absorbent does not need physical energy to separate the particles adhered to the surface matrix.
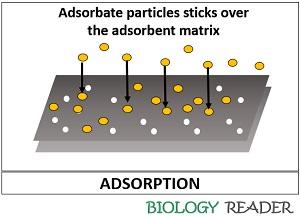
The process of adsorption can be understood by taking an example of an adsorbent as the activated charcoal and adsorbate as the gaseous ammonia. The activated charcoal possesses minute pores, which will allow the gaseous ammonia to stick onto those pores that it becomes easy to separate the adsorbate.
Here, the interaction between the absorbent and absorbate particles is non-persistent, as the particles loosely adhere to the surface of the adsorbent matrix. The absorbate stick to the adsorbent via some physical force of interaction or chemical bond like Van der Waals intermolecular forces or covalent bonds, respectively.
The rate of adsorption is non-uniform, which increases gradually until it reaches an equilibrium state. The heat exchange between the surface and surrounding is exothermic, i.e. energy is liberated.
Types
Physical adsorption: It also refers as Physisorption, in which absorbent matrix and the absorbate particles associate via a weak Van der Waal forces.
Chemical adsorption: It also refers as Chemisorption, in which absorbent matrix and the absorbate particles associate via chemical bond especially covalent bond.
Examples of Absorbent
The key role of absorbent is to dissolute or absorb the particles interacting with it. Some of the examples are mentioned below:
- Some daily life examples of absorbents include household items like towels, paper napkins and paper towels etc.
- Biological processes like skin absorption and intestinal absorption are typical examples, in which a former absorbs the physical energy like sunlight and some chemicals and a latter absorbs the nutrients and water.
- The refrigerant liquid is also an example of absorbent, which absorbs the heat out of the refrigerator.
Examples of Adsorbent
The function of absorbent is to separate the particles interacting with it. Some of the examples include:
- Some common examples of adsorbent include silica gel, activated alumina, activated charcoal, zeolites, activated carbon etc.
- Adsorption of viruses is a biological process, in which a virus attaches to the host cell surface.
- Adsorption chromatography is a molecular technique, which can separate the particles of the liquid or gas adhered to the stationary phase or adsorbent matrix.
Key Differences Between Absorbent and Adsorbent
- Absorbent matrix permits the solid, liquid and gaseous particles to enter into the surface of the matrix. In contrast, adsorbent matrix retain the particles of the dissolved solid, liquid and gaseous medium over the surface of the matrix.
- The absorbent media absorbs the absorbate particles (able to being absorbed into the media). In contrast, the adsorbent matrix separates the adsorbate particles (able to being adsorbed over the surface of medium).
- Absorbent works by a principle of diffusion or osmosis, which allows the specific particles to enter into the matrix. Oppositely, adsorbent medium works by a principle of adhesion, which allows the particles to adhere over the surface of the matrix.
- Absorbent uses a bulk phenomenon, in which the absorbate gas or liquid absorbed throughout into the absorbent matrix. In contrast, adsorbent uses a surface phenomenon, in which the adsorbate particles retains only over the top of the adsorbent medium.
- The absorbed materials get into the absorbent through different phases of matter or some chemical reaction. The adsorbed materials stick to the adsorbent via Van der Waals forces or covalent bond interaction.
Conclusion
Therefore, we can conclude that the absorption and adsorption are the two mechanisms that depend upon the solid or liquid matrix and the dissolved solid, liquid and gaseous particles to be separated.
Hence, the absorption phenomenon makes the use of an absorbent matrix to absorb the particles called absorbate. Similarly, the process of adsorption makes the use of the adsorbent medium to separate the particles known as the adsorbate.
Thus, absorption is a process, where a substance becomes fully saturated within the another substance, while adsorption is a process that allows the binding of one substance over the surface of another substance.