Hanging drop method permits the examination of the living microorganisms, which involves fixation of microbial suspension into a drop of fluid over the glass slide. Therefore hanging drop method is the process, in which the microorganisms are suspended into a drop of fluid. It is a modified version of the wet mount technique.
The shape, size and arrangement of bacteria are easily identifiable in wet mount method, but the bacterial motility becomes difficult to study as the microbial suspension in the well of cavity slide is pressed by the coverslip. Light microscopy makes the use of wet mount method, smear preparation, heat fixing and stain films to make the organism visible to us.
Thus, a hanging drop is a kind of wet-mount method that uses inoculum of bacteria from the liquid broth. It is an important tool to determine the intrinsic movement of the microorganisms, and that’s why used to test the motility of different organisms like bacteria, filamentous fungi and yeasts. All the bacterial cells will show erratic motion, including both motile and non-motile forms under the microscope, which we call as Brownian motion.
But, the self-propulsion in bacteria is identified by either of the following mechanisms like flagellar, gliding, corkscrew and bending type of motion. In hanging drop motility testing, we can see numerous immortalized cells towards the edge of fluid, under the microscopic observation. In this article, we will be discussing the definition, procedure, notes to be considered, applications, advantages and disadvantages.
Content: Hanging Drop Method
Definition of Hanging Drop Method
Hanging drop method is the traditional method for examining the cell motility and morphology by taking the living microorganisms from the liquid media. The hanging drop method works on the principle of wet mount preparation, as it involves subjection of living microorganisms into a drop of fluid. It makes the use of glass slides with one small concave depression towards the centre, a coverslip, petroleum jelly, microbial suspension and sterile inoculating loop. It was first discovered by a scientist named Robert Koch in the year 1878.
Previously, a hanging drop technique was used to examine the Nocardia sp. on liquid paraffin droplets. On further study, the method has been used extensively to demonstrate the bacterial morphology and motility. Later, considering the large drop size in the hanging drop method, scientists started using the micromanipulation technique to get control over the drop size.
Procedure of Hanging Drop Method
The examination of microorganisms in a hanging drop method involves the following protocol:
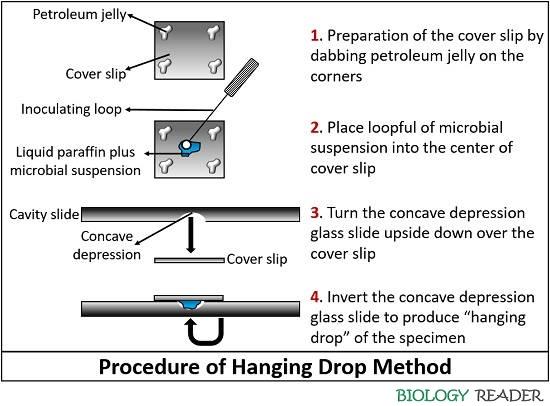
- Take grease-free or clean coverslip and then carefully dab petroleum jelly towards the corner of it by using a toothpick or earbud.
- After that, place a loopful of the microbial suspension on the centre of the prepared coverslip.
- Then, take a clean or grease-free cavity glass slide and turn it upside down. Place the cavity slide in a manner that the circular concavity should be towards the drop of fluid over the coverslip.
- Again turn the cavity glass slide in such a manner that the microbial specimen will found inverted over the concave depression or observed hanging from the coverslip.
- Then put the prepared culture slide on the slide holder of the light microscope and adjust the just in a way that the edge of drop must be visible through the eyepiece.
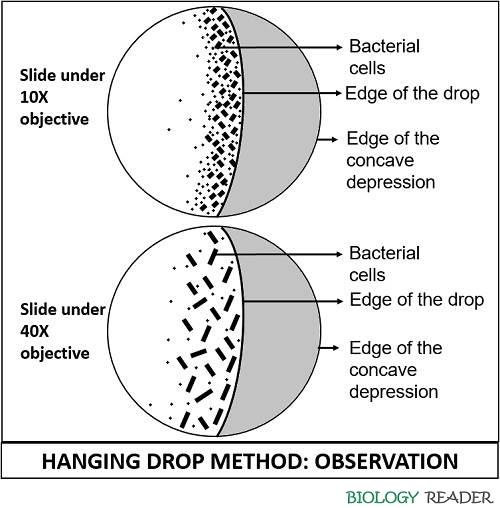
- Use 10X objective lens and close the diaphragm. Then, slowly adjust the coarse focus knob accordingly until you observe a curve that crossing the field of view, in which one half shows the edge of the drop and the other half shows the edge of concave depression.
- Adjust the fine focus knob by looking to the specimen over the slide through the eyepiece, until the edge of the drop appears as a thick dark line.
- Then, look onto each side of the line and focus onto the particulate matter in the fluid suspension. The cells may vary in colour, size and shape.
- After that, use a 40X objective lens for higher resolution and also turn on the diaphragm lever. Then, adjust the light in order to maximize the visibility of the microorganisms.
- After all this set-up, carefully observe the specimen and note down the microscopic properties like the shape, colour, motility of the specimen placed on the glass slide. All the cells will show Brownian movement, but few may possess true motility.
- At last, thoroughly clean the depression slide by putting into a Lysol solution for at least 15 minutes, as the microorganisms remain alive in such slide preparation.
Notes
- Hanging drop method is an aseptic method for examining the specimens from liquid culture instead of a solid culture medium.
- In the hanging drop method, the microbial suspension is wet-mount rather than subjecting it to the methods like heat-fixing, smearing, staining etc.
- It is extensively used to study bacterial shape and arrangement and presence of flagella.
- Specimens in the hanging drop method will show Brownian movement, due to which the microscopic objects in the fluid will swim erratically through the kinetic energy possessed by the molecules in the surrounding fluid.
- The true mobility is observed through the multi-directional movement of bacterial cells to longer distances, instead of the cells moving back and forth. The bacterial motility can be observed under 10X and 40X objective, which is shown in a diagram. In a hanging drop method, 10X objective is initially used to focus the microscopic image, then later the objective is raised to 40X to get a magnified view of the sample taken and to distinguish between the motile and immotile cells.
- The petroleum jelly used on the corner of the coverslip acts as a sealing material between the coverslip and the concave depression glass. Besides, it also reduces the evaporation and excludes the effect of air currents.
- Overuse of petroleum jelly can give false results, as it may squeeze towards the centre of the drop containing microorganisms or may squeeze out of the edges and can stick to the objective lens of the microscope.
- The disposal of the slides should be carefully done, as after dipping the slides in Lysol solution it must be autoclaved and can be reused. The coverslips should be discarded and cannot be reused.
Applications
The morphology of spiral bacteria can be explicitly studied in hanging drop method, as its shape becomes distorted in the heat fixing method. Spiral bacteria like spirochetes need to be examined in a living state, and there shape and arrangement can be well studied under a dark field microscope.
Bacterial motility or mobility can be well studied by employing a hanging drop method, in which a bacterial cell can freely move in the liquid medium.
The cytological changes that occur during the cell division, spore formation and germination of the bacteria are the events that need to be studied in a living condition or hanging drop method. The cytoplasmic inclusions, including vacuoles, granules etc. are easily noticeable by using this method.
Advantages
- It is an important tool to study the bacterial motility along with the shape, size and arrangement of the bacteria.
- It does not distort the cell shape and arrangement.
- Besides, the hanging drop method provides a better view of motility in bacteria than the wet mount method.
- It is also helpful in the classification of the bacteria, whether they are motile or immotile.
- The Brownian movement can be studied through this method, which causes erratic movement of the bacterial cells in the field of view due to the bombardment of water molecules.
- The petroleum jelly used in this technique seals the coverslip to the cavity slide that helps in the study of the tested specimen for many times.
Disadvantages
- It is risky for the study of pathogenic bacteria in a living condition.
- The depression slide is cost-effective, and the coverslip is fragile to work with.
Conclusion
Therefore, we can conclude that the hanging drop method is the best way to study the different events of the organism in a living state, the mobility, shape and arrangement of the bacterial cells. Hanging drop method is a kind of motility test, which is performed by taking the microorganisms from liquid media on the glass slide having indentation towards the centre.