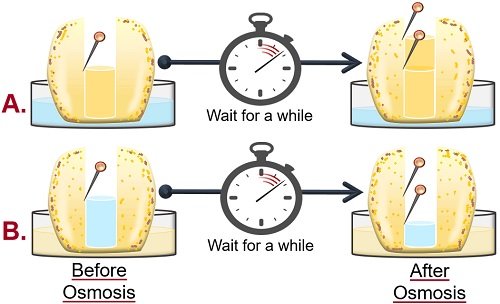
A study of osmosis can be done using a potato osmometer. Osmosis is a phenomenon in which water moves from high solvent to low solvent concentration. The movement of water occurs between two compartments, separated by a semipermeable membrane.
The cell membrane of living organisms behaves as a semipermeable or selective membrane. The permeability of a selective membrane differs based on the size, charge and mass of different molecules.
Biological membranes are impermeable to large biomolecules and polar molecules like ions. But, non-polar molecules (lipids) and small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide etc.) can cross the selective barrier.
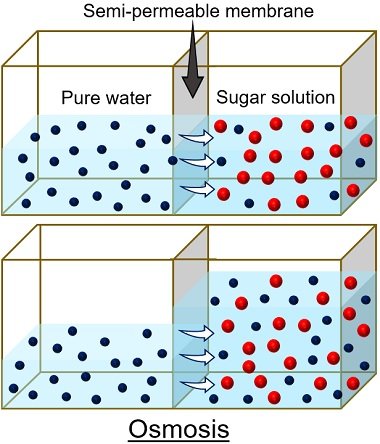
Water is the solvent that travels down or up the cell concentration gradient through osmosis. We can study water diffusion by creating two compartments and a semipermeable membrane in between.
The difference in the concentration of solutes or solvents between two compartments is the driving force responsible for water movement. Here, we need to note that only solvents can pass the selective barrier, not solutes.
Thus, the diffusion or distribution of water is related to osmosis. This post describes the meaning, requirements, procedure and results of the potato osmometer experiment.
Content: Study of Osmosis by Potato Osmometer
Potato Osmometer
It is a common experiment to demonstrate both endosmosis and exosmosis using a potato. Using a potato Osmoscope, we can study osmosis in a living system.
Here, a potato is used because the porous outer surface of the potato acts as a selective membrane.
- The contents within the cell form one compartment.
- The solution surrounding the cell forms another compartment.
Thus, a selective membrane separates two compartments and allows the process of osmosis.
To study endosmosis, a concentrated sugar solution is poured into the cavity of the potato tuber, which is kept in the Petri plate containing water.
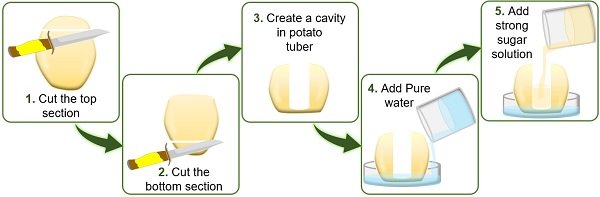
The solution level inside the cavity of the potato tuber increases due to:
- High solvent concentration in the cell surrounding.
- Low solvent concentration in the cavity of potato tuber.
Following the rule of osmosis, water in the cell surrounding enters the tuber cavity via the cell membrane.
To study exosmosis, water is poured into the cavity of the potato tuber, which is kept in the Petri plate containing concentrated sugar solution.
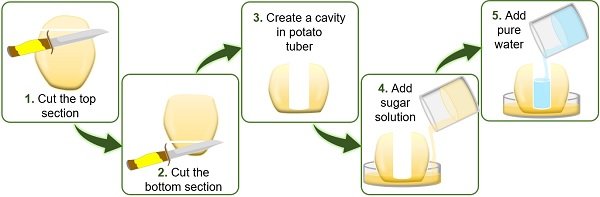
The water level inside the cavity decreases due to:
- High solvent concentration in the cavity of potato tuber.
- Low solvent concentration in the cell surrounding.
Following the rule of osmosis, water in the potato cavity enters the surrounding solution via the cell membrane.
Materials Required
To perform the experiment, we need the following things:
- Peeled off potato
- Knife
- Pure water
- Concentrated sugar solution
- Petri plate
- Pins
Video: Study of Osmosis
Procedure
To perform the potato osmometer experiment, we need to follow the given procedure:
- First, peel off the large-sized potato using a peeler or knife.
- Then cut the upper and lower portions of the peeled potato using a knife. Through this step, we can easily place the potato on the Petri plate.
- Using a knife, make a cavity from the centre of the potato deep into the bottom, leaving some space. Here, the bottom of the potato will function as a selective membrane.
- Then, keep the potato on the Petri plate.
- To study endosmosis, pour water into half of the Petri plate. Next, pour the concentrated sugar solution into half of the cavity created in the potato.
- To study exosmosis, add concentrated sugar solution on the Petri plate and water into the cavity of the potato tuber.
- Then, fix a pin into the potato tuber-A and B to mark the level of sugar solution and water added into the cavity.
- Leave the plate undisturbed for some time until you notice any change.
Observation
- Observe the level of sugar solution in the cavity of potato tuber-A.
- Notice the level of water in the cavity of the potato tuber-B.
Potato Osmosis Experiment Results
- The level of sugar solution in the cavity of potato tuber-A increases. It occurs because the water in the Petri plate will move towards the cell with a high solute or low solvent concentration. This experiment shows endosmosis, as water goes into the cell or potato tuber.
- In contrast, the level of water in the cavity of potato tuber-B decreases. Here, water in the cavity moves toward the solution in the Petri plate due to the high solute concentration in the surrounding. This experiment shows exosmosis as water leaves the cell or potato tuber.
Precautions
- The cavity should be deep enough by leaving a minimum thickness at the bottom.
- The sugar solution should have a high osmotic concentration.
Conclusion
The water movement from the Petri plate to the potato cavity or vice versa is due to the difference in the solvent or solute concentration between the two compartments.