The bacteriological incubator prominently cultivates a wide range of bacteria under controlled conditions. It has extensive use in research and medical laboratories.
Bacteriological incubators provide an enclosed environment for the growth of bacteria. They work under the ideal temperature range of 35°C to 37°C.
This post describes the bacteriological incubator’s meaning, principle, operation, and uses. Also, we will discuss the construction of the bacteriological incubator.
Content: Bacteriological Incubator
Meaning of Incubator
The incubator provides an enclosed chamber to cultivate uni and multicellular species. Besides, it maintains different cell or microbial cultures under ambient temperature.
- The thermostat regulates the temperature within the incubator. And, the range of temperature may vary from five to eighty degrees Celsius.
- Not only temperature but the incubator also maintains humidity, oxygen and carbon dioxide. Such factors are necessary to maintain the cell or microbial cultures.
A controlled environment is conducive to cultivating, maintaining and studying the desired organism. Thus, incubators have much experimental and research use.
They have broad applicability in microbiology, cell biology and molecular biology. Biological oxygen demand, bacteriological and CO2 incubators are three common types. In this context, we will only discuss the bacteriological incubator.
Bacteriological Incubators
They provide an insulated chamber to promote bacterial growth under stable conditions. They provide a constant supply of hot air over racks where we can keep the bacterial culture plates.
Principle
The working of a bacteriological incubator depends upon thermo-electricity. A thermostat at the incubator’s top regulates a desirable temperature within the chamber.
The bacteriological incubators work by using a heating system only. Due to this reason, we call such incubators “heated incubators”.
The term “Bacteriological incubator” itself clears that it only incubates bacteria.
- It maintains a desirable temperature range of 10°C above ambient to 60°C.
- Most bacteria grow best at a temperature of 37 °C.
The bacterial growth within the bacteriological incubator is independent of the external environment. In general, the incubator utilizes heating and no-heating cycles.
- During the heating cycle, the thermostat heats the incubator.
- The incubator radiates heat outside during the no-heating period.
Uses
Bacteriological incubators have the following applications:
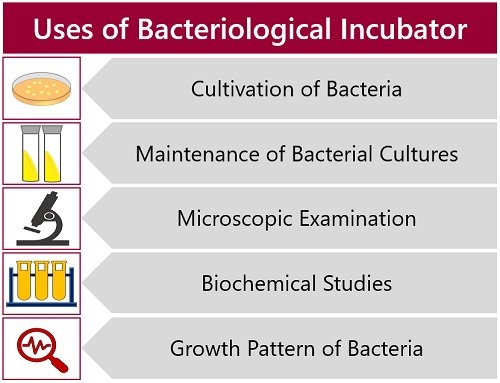
- Bacteriological incubators help in growing bacterial cell cultures.
- It also helps in maintaining the culture of bacteria for future use.
- After incubation, you can isolate the bacteria for microscopic examination.
- Besides, you can perform biochemical tests of the isolated bacteria. It helps in determining the type and species of the isolated bacteria.
- Within the incubators, you can grow bacteria at different temperatures. It helps in studying the growth pattern of bacteria.
Handling Procedure
Let us look into the points on handling the bacteriological incubator.
Procedure
- First, take out the culture plates from the incubator that are of no use.
- Label the Petri plates after inoculating bacteria into the growth media.
- Then, you can keep the culture plates upside down over the perforated racks.
- Afterwards, close the door of an incubator. This aids in the growth of bacteria within an isolated environment. Thus, the external factors do not hamper bacterial growth.
- Switch on the main power switch to supply electricity. Set the desired temperature, depending on the growth conditions of cultured bacteria.
- After some time, the temperature within the incubator stabilizes. The blower at the top circulates the hot air throughout the cabinet.
- Take out the Petri plates and tubes containing the bacterial culture after 24 to 48 hours.
Parts of the Bacteriological Incubator
Following are the components of the bacteriological incubator:
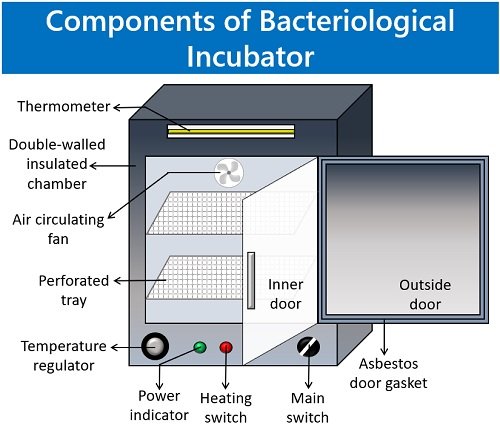
Cabinet
The cabinet is the main body of the incubator. It comprises the double-walled enclosed chamber. The capacity ranges from 20 to 800L.
- Stainless steel sheets constitute the outer wall.
- Aluminium forms the inner wall.
Glass wool covers the space between the two walls. As well as, it provides insulation. The insulation prevents heat loss, thereby reducing electricity consumption. It ensures the smooth working of the device.
The sides walls of the incubator have some ridges that hold the shelves inside the incubator.
Door
A door is present in all incubators to close the insulated cabinet.
- The asbestos door gasket is present between the door and the cabinet. It serves as an airtight seal that insulates the interior of the chamber from the outside air. Thus, the external factors do not interrupt the bacterial growth inside the cabinet.
- The inner glass door enables you to see the sample from the outside. It guarantees temperature stability.
- A handle on the outside door helps to lock the cabinet.
Control Panel
The outer body of the incubator has a control panel with all the switches and indicators. You can control the parameters necessary for bacterial growth through the control panel.
- The main switch allows you to switch on or off the power supply.
- Through the temperature regulator knob, you can adjust the temperature inside the incubator.
- Using a heating switch, you can also control the heat.
- A thermostat indicates the desired temperature within the incubator.
Perforated shelves
- You can keep the culture tubes and plates over these perforated shelves. Perforations aid in the uniform movement of hot air within the incubator.
- These shelves are removable or adjustable.
Maintenance
Using an incubator many times may contaminate the incubator. And you may likely get erroneous results. So, you must follow a strict cleaning schedule for your unit. Some necessary precautions to follow are:
- Always wear gloves and a mask while cleaning the chamber.
- Daily clean the interior of the chamber, including shelves and other removable parts. You can scrub off the adhering dust using tissue paper.
- Depending on the application, you can practise disinfection or complete sterilization.
- Use an ideal disinfectant that:
- It should not cause corrosion.
- It won’t harm your cell cultures.
- A quaternary ammonium disinfectant is best for many applications.
- Remember to clean the outside of the unit, especially the door handle.
- Clean the fan and fan wheels every few months.
Conclusion
So, bacteriological incubators depend upon the dry heat principle. The bacterial culture grows within the incubators under constant temperature. Also, other favourable conditions are maintained inside.
The majority of bacteria grow best between 35 to 37 degrees Celsius for an incubation period of 24 to 48 hours. The incubation temperature and time may vary. The variation is due to the different types and growth patterns of bacteria.