Biosphere reserves are one of the methods of in-situ biodiversity conservation, which are the largest protected area covering more than 5000 sq. km. These cover more land area than the other methods (National parks and wildlife sanctuaries) of the in-situ biodiversity conversation. They are also termed “Biodiversity reserves“.
It conserves biodiversity by protecting plant, animal and wildlife resources. Flora and fauna within the biosphere reserve flourish in their natural habitats. Besides conservation, it also aims to develop different approaches for the sustainable use of natural resources by humans.
It also supports research, education and training to minimize biodiversity loss and develop strategies to conserve biodiversity and ecosystem. Therefore, biosphere reserves are the large protected regions where all the biotic components of the ecosystem (plants, animals, humans etc.) coexist by respecting each other’s needs.
This post describes the definition, objectives, origin, key facts, structure and functions of the biosphere reserve. You will also get to know the names of all the 18 biosphere reserves in India.
Content: Biosphere Reserves
Definition of Biosphere Reserve
It refers to the natural sites that foster the cooperative relationship between the people and nature to establish sustainable development in social, cultural, ecological and economic areas through continuous monitoring, research and training. Biosphere reserves primarily support biodiversity conservation, development and education programmes.
Core, buffer and transition zones are the three distinct regions of the biosphere reserve. The core zone is the highly protected area around which the additional land area (buffer and transition zones) supports people’s livelihood.

What is Biosphere?
The biosphere is the region occupied by the living system where the different living communities coordinate and coexist within the ecosystem. Sometimes, it is also called the ecosphere. Eduard Suess first coined the term “Biosphere”. Lithosphere (rock), atmosphere (air), hydrosphere (water) and cryosphere (ice) contribute to the layers of earth. Therefore, the biosphere contributes to the zone of life on earth.
Objectives
Biosphere reserves are established to fulfil the following demands related to the environment’s biodiversity and conservation.
- They conserve the biodiversity of flora and fauna within the natural ecosystem.
- The biosphere reserve ensures sustainable development of the environment through multi-faceted research and monitoring.
- They also provide education and training facilities.
Origin
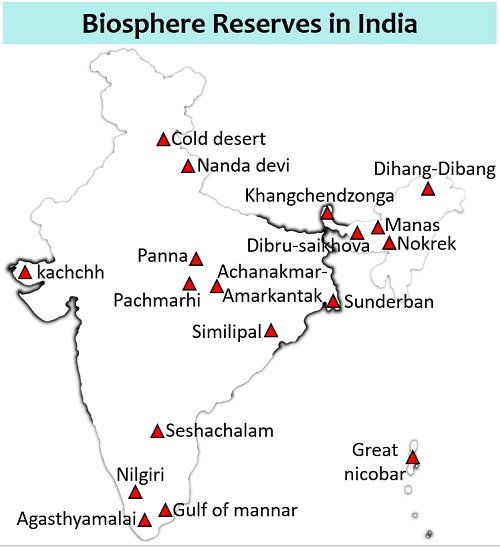
Biosphere reserves are the designations nominated by the ICC of UNESCO under the (MAB) Man and Biosphere programme launched in 1971. MAB is an intergovernmental scientific programme. The Indian government has established 18 biosphere reserves recognized by the IUCN (International Union for conservation of nature). The list of all eighteen biosphere reserves is mentioned in the table below.
| Year of Recognition | Biosphere Reserves of India | State |
|---|---|---|
| 1986 | Nilgiri | Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka |
| 1988 | Nanda Devi | Uttarakhand |
| 1988 | Nokrek | Meghalaya |
| 1989 | Gulf of Mannar | Tamil Nadu |
| 1989 | Sundarbans | West Bengal |
| 1989 | Manas | Assam |
| 1989 | Great Nicobar | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| 1994 | Similipal | Odisha |
| 1997 | Dibru-Saikhova | Assam |
| 1998 | Dihang-Dibang | Arunachal Pradesh |
| 1999 | Pachmarhi | Madhya Pradesh |
| 2000 | Khangchendzonga | Sikkim |
| 2001 | Agasthyamalai | Kerala, Tamil Nadu |
| 2005 | Achanakmar-Amarkantak | Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh |
| 2008 | Rann of Kutch | Gujarat |
| 2009 | Cold desert | Himachal Pradesh |
| 2010 | Seshachalam Hills | Andhra Pradesh |
| 2011 | Panna | Madhya Pradesh |
Form 18, India has 12 MAB UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) sites. The basic idea behind the biosphere designation is to establish a balanced relationship and equality between humankind and nature.
Key Facts
- ICC (International Coordinating Council) of UNESCO introduced the designation of biosphere reserves.
- The National Biosphere Reserve Programme (1986) ensures the participation of local inhabitants for effective management through sustainable use.
- India is one of the megadiversity regions on the globe possessing 18 biodiversity reserves.
- Biosphere reserve serves as the site through which one can predict the consequences of today’s actions on tomorrow’s world, thereby allowing people to efficiently manage the natural resources for the well-being of their own and the ecosystem.
- It is the international or global approach that develops international understanding to efficiently manage the natural resources through social, cultural and economic development.
- It supports the development of the ecosystem from the local to the international level through continuous monitoring, educational and research programmes.
- The biosphere reserve aims to conserve the genetic diversity of the ecological zones, or it has an ecological significance.
- It generally exists as the large protected areas of land, coastal environment or both.
- People living within the biosphere are the integral components of the biosphere reserves, as they participate in sustainable development, conservation, management and maintenance of the environment.
- Biosphere reserves possess the central non-manipulative core area and flexible buffer and manipulative transition zones surrounding it.
Importance of Biosphere Reserves
Biosphere reserve mainly targets the three interdisciplinary areas:
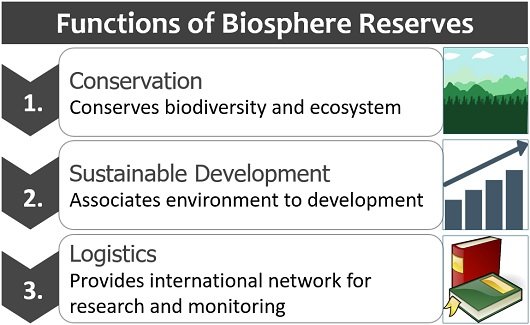
Conservation: It conserves the genetic, species and ecosystem biodiversity in the natural environment. In addition, it fosters the traditional means of resource management systems. Biosphere reserves monitor the naturally occurring changes and changes due to the anthropological activities on special and temporal scales.
Development: It ensures sustainable development of the environment and sustainable use of the environment’s natural resources. The biosphere reserve supports the environment’s social, cultural, ecological and economic development through strategies to improve and manage natural resources.
Logistics: It supports research, monitoring, education and training concerned with the causes of biodiversity loss and its management strategies. In addition, it is underpinning different cultural programmes to encourage the community spirit in managing natural resources. Biosphere reserves also allow an exchange of knowledge and information regarding the issues of conservation and development.
Biosphere Reserve Zones
There are three distinct zones of the biosphere reserve.
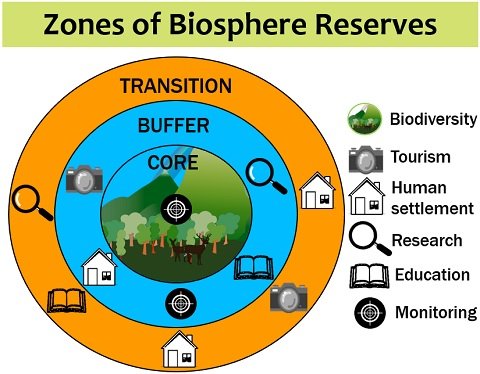
Core Zone
It is the innermost region conserving biodiversity. Here, human activities are highly prohibited. Endemic plants and animals reside within this layer. The specialists can regularly monitor the activities within the core zone to maintain the sustainability of that particular ecosystem.
Core zone contributes to managing the landscapes, ecosystem, genetic and species variation. It is protected and regulated under the Wildlife Protection Act. Thus, the core zone serves as a legally protected and undisturbed region free from human interference.
Buffer Zone
It is an intermediate zone between the core and transition zones. The buffer zone lies in close proximity or adjacent to the core zone. It allows minimal human interference. Only researchers, legal advisories, people of tribal communities etc., can study, monitor and protect the core zones.
Therefore, the buffer zone has less intensive human interference that would not harm the core region’s norms but rather help protect it. It supports site-specific education and training to manage natural vegetation, agricultural land, forests etc. Besides this, the buffer zone also provides space for tourism and recreation facilities.
Transition Zone
The manipulation, flexible or transition zone has a larger outer area. It supports the sustainable use of natural resources. People within the transition zone, including local communities, civil associations, cultural groups and other stakeholders, cooperate and work together.
Living communities of transition zone use resources in a sustainable manner. It improves the economic well-being of the local people who have a hand in managing the resources through fisheries, farming and forestry.
Thus, the transition zone fosters harmonious integration of people and reserve management. It encourages social, cultural and economic development through the exchange of knowledge, continuous monitoring, research, participation of local people, and by respecting cultural values etc.
Conclusion
Biosphere reserves are the natural sites that help in testing and demonstrating sustainable management of land, natural resources, and biodiversity. Biosphere reserves form a World Network that permits the exchange of knowledge, experiences and personnel.
We can conclude that the biosphere reserve safeguards the organisms (plant and animal species) within the specific area. It develops strategies for the sustainable use of land and natural resources and the mutual benefit of humankind and nature.