The difference between cerebrum and cerebellum is mainly due to the following properties like size, constitution to brain and location. They both contribute to the human brain or central nervous system and plays an integral role in our everyday life. The size of the cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, while cerebellum is much smaller or the second largest part of the brain.
Cerebrum constitutes about 83% of the total brain, whereas cerebellum constitutes about 11% of the brain. The cerebrum is a part of the brain located in the forebrain, whereas cerebellum is located in the hindbrain.
Cerebrum and cerebellum are the two major parts of the brain, which remain isolated through dura matter and communicate through the brain stem. Here, you will get to know a detailed comparison of the topic through the comparison chart, and the key differences explained in this article. Also, the definition and the structural components of the cerebrum and cerebellum are discussed.
Content: Cerebrum Vs Cerebellum
Comparison Chart
| Properties | Cerebrum | Cerebellum |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Percentage in human brain | 83% | 11% |
| Location | Forebrain | Hindbrain |
| Arbor vitae | White matter does not form arbor vitae | White matter forms arbor vitae |
| Hemisphere separation | Separated by longitudinal cerebral fissure | Separated by median vermis |
| Cortical layers | It is having 6 cortical layers | It is having 3 cortical layers |
| Lobes | Cerebrum is divided into four lobes | Cerebellum is divided into three lobes |
| Origin | Formed late during the evolution of human | Formed early during the evolution of human |
| Neuron percentage | Comparatively less than the cerebellum | It alone consist of 50% of total neurons |
| Activity control | Controls voluntary action, motoric functions, cognition etc. | Controls body movement, languages, emotions etc. |
| Fundamental role | Play a fundamental role in human senses | Play a fundamental role in maintaining body equilibrium |
Definition of Cerebrum
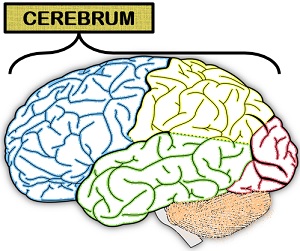
It can define as the largest part (9 times) of the brain, which constitutes about 80% of the brain’s total mass. The cerebrum is divided into two cerebral hemispheres, namely right and left hemispheres. A grey matter and white matter encircles each cerebral hemisphere. Frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobe are the four lobes exist with each cerebral hemisphere. Cerebrum performs a functional role in learning, speech, and emotions.
Definition of Cerebellum
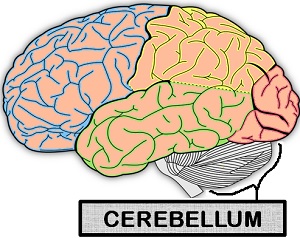
It can define as the second largest part of the brain, which only constitutes 11% of the total brain. Like the cerebrum, the cerebellum also comprises two hemispheres and consists of outer grey matter and inner white matter. The cerebellum contains 50% of the brain’s neuron and specialized cells. It is located on the back of the brain.
Each cerebellum hemisphere consists of three lobes, namely anterior, posterior and flocculonodular lobe. Previously, the cerebellum was considered a motor structure because of its function in motor learning, cognitive functions, maintenance of balance and posture etc.
Structure of Cerebrum
Cerebral is a part of forebrain found in the upper cranial cavity of the brain. It consists of the following structural elements:
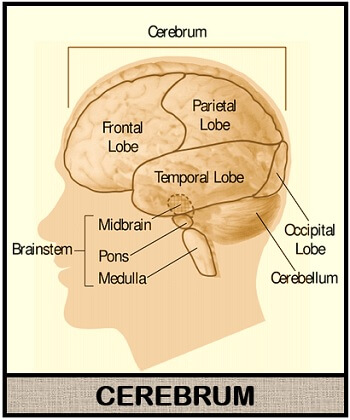
Cerebral hemisphere: There are two deep furrows, namely left and right cerebral hemispheres. The longitudinal fissure separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The left hemisphere controls the body’s left side, and the right hemisphere controls the body’s right side.
Corpus callosum functions as a communicating link between the two cerebral hemispheres by transferring the messages between the two. A grey matter comprises numerous “Nerve-cells” that encircle each cerebral hemisphere. Inside the grey matter, white matter is present which possesses “Nerve fibres”.
The nerve fibres in the white matter carry signals between the nerve cells and the other parts of the brain and body. Each cerebral hemisphere consists of four lobes like frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobe that perform the following functions mentioned in the table given below.
| Cerebral lobes | Functions |
|---|---|
| Frontal lobe | Voluntary movement |
| Parietal lobe | General sensation and feeling |
| Occipital lobe | Processing of visual information |
| Temporal lobe | Auditory processing |
Cerebral cortex: It is a highly grooved region. It is the structural element of the cerebrum that increases the surface area of the brain. Inside cerebrum, there is a bulk of “Neocortex”. The neocortex is a six-layered structure of cerebral cortex that participates in higher information processing.
Gyrus: In the cerebrum, there is a bulk of elevated regions called “Gyri”. Gyri increase the surface area of the cerebrum and separate lobes based on their functional roles. Gyrus takes part in motor functions of the frontal lobe is called “Precentral gyrus”. Gyrus involved in the sensory functions of the parietal is called “Postcentral gyrus”.
Sulcus: Central sulcus exists as a deep groove that isolates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe.
Structure of Cerebellum
Cerebellum possesses two hemispheres like cerebrum. It appears as a highly folded structure present underneath the occipital and temporal lobe of the cerebrum. Cerebellum is present below the dense mass of the cerebral cortex. It is present posterior to pons and above the brain stem. So, the cerebellum is the part of “Rhombencephalon region” which is also called “Hindbrain”.
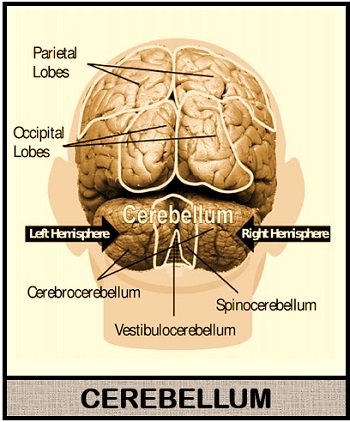
Cerebellum hemisphere: Cerebellum develops after the metencephalon division, and it becomes separated by the four lobes of the cerebrum via “Tentorium cerebelli”. “Vermis” is the midline area that allows communication between the two cerebellum hemisphere. Like the cerebrum, it also contains grey as well as white matter. Anterior, posterior and flocculonodular lobe are the three lobes found in the cerebellum. “Primary fissure” and “Posterolateral fissure” separates the anterior, posterior and flocculonodular lobe.
Zones: A cerebellum has three zones, namely vermis, intermediate and lateral hemisphere.
- Vermis zone: It is the midline area, which connects the two cerebellum hemispheres.
- Intermediate zone: It is present intermediate to either side of the vermis zone.
- Lateral hemisphere: It is present lateral to the intermediate zone.
The cerebellum plays a fundamental role in motor functioning where a brain is giving signals to rest of the body parts to carry out a particular task, due to which it is also called “Little brain”.
Key Differences Between Cerebrum and Cerebellum
- The cerebrum seems larger in size, accounting for about 83% of the total brain, whereas cerebellum seems comparatively smaller, contributing to about 11% of the total mass.
- The cerebrum is associated with the “Forebrain or Prosencephalon”, while the cerebellum is associated with the “Hindbrain or Rhombencephalon”.
- There are six cortical layers present in the cerebrum and three in the cerebellum.
- The cerebrum possesses four lobes, namely frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobe, unlike cerebellum that possesses three lobes, namely anterior, posterior and flocculonodular lobe.
- The cerebrum’s primary function includes thinking related processes, whereas cerebellum performs a fundamental role in body movement and coordination.
Conclusion
Both cerebrum and cerebellum are the two structures of the central nervous system. The cerebrum controls the thinking related processes (like reasoning, learning, planning, judging), emotions or impulse control, visual memory, verbal memory, and interprets the sensory information. Cerebellum monitors the coordination in muscle movement. Therefore, cerebrum and cerebellum are the two different structures that complement each other in a way and coordinate to help us perform tasks and memorize things.