The difference between plasmolysis and deplasmolysis is mainly due to factors like:
Water movement: In plasmolysis, the movement of water is from the cell protoplast to the surrounding and deplasmolysis cause movement of water into the cell protoplast.
Water potential: Plasmolysis occurs due to the low water potential of the surrounding than the cell cytoplasm, whereas deplasmolysis occurs due to the high water potential of the surrounding than the protoplasm.
Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis are the two subtypes of osmosis, depending on the water potential difference within the protoplast and cell surrounding.
Content: Plasmolysis Vs Deplasmolysis
Comparison Chart
| Properties | Plasmolysis | Deplasmolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Plasmolysis is a process in which the plasma membrane enclosing the cellular constituents become shrinked by the loss of water | Deplasmolysis is a process in which the plasma membrane enclosing the cellular constituents get swelled by the movement of water into it |
| Water movement | Water exits the protoplasm to the cell surrounding | Water enters the protoplasm from the cell surrounding |
| Net flow of water | Positive | Negative |
| Solution | It occurs in a hypertonic solution | It occurs in a hypotonic solution |
| Solute concentration within the cell | It is relatively low | It is relatively high |
| Solute concentration of the surrounding | It results due to high solute concentration of the cell surrounding | It results due to low solute concentration of the cell surrounding |
| Water potential of the cytoplasm | Here the cytoplasm possesses high water potential | It has relatively lower water potential |
| Water potential of the surrounding | It is relatively low | It is comparatively high |
| Effect on water potential on the cell | Water potential of the cell decreases by the increasing solute concentration | Water potential of the cell increases by the reduced solute concentration |
| Result | It causes wilting of leaves due to loss of turgidity, which results by the inadequate water in the surrounding | Plant restores the turgidity when there is enough water concentration outside the plant cell |
| Cause | Exosmosis | Endosmosis |
| Osmotic pressure | Very low (due to water movement from the cytoplasm) | Very high (due to water movement into the cytoplasm) |
| Osmotic potential of water | Increases in case of plasmolysis, i.e. in a hypertonic solution | Decreases in case of deplasmolysis, i.e. in a hypotonic solution |
| Effect on protoplasm | The protoplasm becomes shrivelled, i.e. the plasma membrane segregates from the cell wall | The protoplasm becomes turgid or swelled, i.e. the plasma membrane returns to its normal state |
| Example | RBCs in a salt solution | RBCs in a distilled water |
Definition of Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis can define as the exosmosis process, which results in a net movement of water into the surrounding from the cell protoplasm when put in a hypertonic solution. It indicates the high concentration of solute in the cell surrounding than the cell protoplasm and high water concentration of the cell sap than the surrounding.
Thus, the water potential of the cell in a hypertonic solution will decrease due to the high solute concentration of the surrounding. As a result, the cell loses up its water and becomes shrivelled. Thus, the net movement of the water is towards the region of low water concentration, i.e. the cell surrounding.
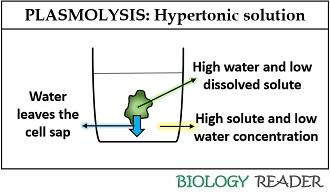
It is a reversible process, in which the cells may restore the turgidity when placed inside the hypotonic solution (high water concentration). If the plasmolysis persists longer, then the cell wall collapses completely (cytorrhysis) and finally leads to apoptosis.
Definition of Deplasmolysis
Deplasmolysis can define as the endosmosis process, which results in movement of water into the protoplasm from the cell surrounding in a hypotonic solution. It indicates the low concentration of solute in the cell surrounding than the cell sap and high water concentration of the surrounding than the cell sap.
Therefore, the water potential of the cell in a hypotonic cell increases because of low solute concentration in the cell surrounding. As a result, the cell takes up water from the surrounding and becomes turgid.
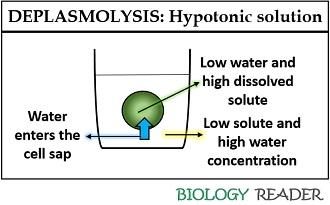
Thus, the net movement of the water towards the direction of low water or high solute concentration, i.e. the cell sap. It is also a reversible process, in which a cell can again lose its turgidity when placed in the solution having low water and high solute concentration.
Key Differences Between Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis
- Plasmolysis is the contraction of the cell sap, while deplasmolysis is the condition that causes cell turgidity.
- Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis occur when the cell is out in a hypertonic and hypotonic solution, respectively. The difference between hypertonic and hypotonic solution is due to the difference in solute and solvent concentration. A hypertonic solution has high solute concentration, i.e. the water concentration will be low, and the hypotonic solution has low solute concentration, i.e. the water concentration will be high.
- As both plasmolysis and deplasmolysis are the types of osmosis, the net movement of water must be towards the low concentration of solute. As a result, water moves into the cell sap in case of deplasmolysis, where the solute concentration is low. Oppositely, the water passively diffuses into the cell surrounding in case of plasmolysis, where solute concentration is low.
- The net flow of water is the movement of water to the direction of high solute concentration, or we can say in the direction of low water concentration. Therefore, the net movement of water in plasmolysis will be positive, as the water flows from the cell sap to the surrounding (low water concentration) across the concentration gradient. Similarly, the net movement of water will be negative in the case of deplasmolysis because the water enters the cell sap from the cell surrounding, down the concentration gradient.
- Deplasmolysis occurs as a result of low water potential of the surrounding, whereas plasmolysis results due to the high water potential of the cell surrounding. This results in a very low osmotic pressure during plasmolysis and high during deplasmolysis.
- Due to the high solute (salt, sugar, etc.) concentration, the cell releases water and becomes plasmolyzed or shrivelled. Oppositely, the low solute concentration will allow water to enter the cell, which later becomes turgid.
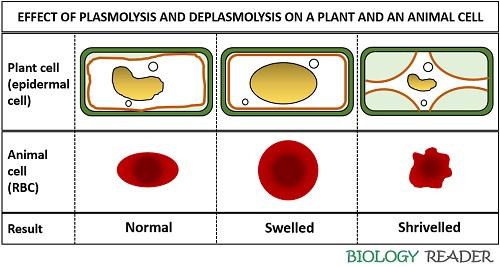
- Plasmolysis is a type of exosmosis, in which water releases out of the semipermeable cell membrane to the surrounding. In contrast, deplasmolysis causes water movement into the cell from the surrounding through the semipermeable membrane that eventually makes the cell turgid.
Similarities
Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis are the two main events, which also share some similarities like:
- Both the events occur as a result of water movement across the selective membrane.
- Plasmolysis and deplasmolysis are the two subtypes of osmosis.
- Both processes occur due to the difference in water potential.
- Both plasmolysis and deplasmolysis cause changes or affect the selective barrier, i.e. the plasma membrane.
Conclusion
Therefore, we can conclude that the plasmolysis and deplasmolysis are the types of osmosis, where each differs in the solute concentration, water concentration, water potential etc. Through both the processes, we can study the effect of high and low solute concentration to the plasma membrane. The effect of exosmosis and endosmosis on the cell mass of the varying cells can also be studied.