Watermelon and Muskmelon are genetically related but have many differences in physical traits. Now the question is, what is the main difference between watermelons and muskmelons if they belong to the same family? Here is the simple answer we can give you right away.
The significant difference between them is seeds. Watermelon seeds are scattered inside the fruit, whereas muskmelon seeds reside within a fruit’s central seed cavity. Apart from that, both look very different in colour, texture, taste, size, weight etc.
They are ultimate summer fruits by excellence. Due to their high water content, watermelons and muskmelons are the best fruit choices in summers. Both fruits provide a source of refreshment and quench your thirst during hot summer days.
This post explains the key differences between watermelon and muskmelon and the comparison chart. Also, it highlights the definition, physical traits and similarities between the two.
Content: Watermelon Vs Muskmelon
Comparison Chart
| Properties | Watermelon | Muskmelon |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Citrullus lanatus | Cucumis melo |
| Meaning | It is a large, oblong fruit with hard, striped green skin and red pulp with many pips inside | It is a large, oblong fruit with ribbed, netted or rough skin and yellow or orange pulp |
| Colour of Fruit Rind | Green to dark green | Muskmelon skin appears beige, green, or sometimes yellow |
| The Pattern of Striations on Fruit Skin | Watermelon skin has green and dark green stripes | Muskmelon has a beige coloured netted rind |
| Rind Thickness | Thicker | Comparatively thinner than the watermelon skin |
| Rind Texture | Smooth | Rough |
| Colour of Flesh | Pink to red watermelons are common, while there are other varieties too | Yellow to orange muskmelons are commonly available, but there are also different varieties |
| Texture of Flesh | On ripening, texture of watermelon becomes grainy and dry | On ripening, muskmelon becomes soft consistency and juicy texture |
| Flavour of Flesh | Watermelon boasts a triad of flavors like bitter, sweet, and sour | It has a sweet and musky aroma |
| Colour of Seeds | Black and some white seeds | Beige coloured seeds |
| Arrangement of Seeds | Numerous seeds are dispersed throughout the flesh | Many seeds are located in the central seed cavity of the flesh |
| Weight | Watermelon generally weighs 3-4 kg | Muskmelon weighs about 1.5-2 kg |
| Shape | Oval or Spherical | Round to Ovate |
| Pigment responsible for the fruit pulp | Lycopene | Beta-carotene |
| Water Content | 92% | 90% |
| Salt Content | Watermelons have a low salt concentration | Muskmelons have a relatively high salt concentration |
| Sugar Content | Comparatively lower than the muskmelons | Sugar content is quite high in muskmelons |
| Flowering Pattern | Monoecious (Andromonoecious also present, but less in number) | Andromonoecious (Monoecious also present, but less is number) |
Definition of Watermelon
Watermelons are succulents or edible fruits with hard, smooth, striped rind and fleshy pulp with many pips inside. They belong to the gourd family (Cucurbitaceae), considered cucurbits or vine plants.
Watermelons are edible fruits cultivated worldwide in favourable tropical to temperate regions. There are more than 1000 varieties of watermelons, including some seedless varieties.
Watermelon vines are annual plants, having only one growing season. They are native to tropical Africa. Watermelon vines grow on the ground and have a prostrate or climbing habit. You can see the physical traits of the watermelon illustrated in the picture below.
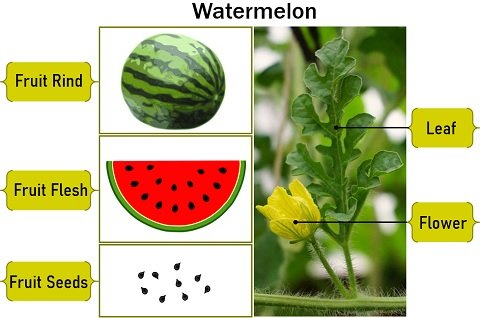
Vines: Watermelon vines have unisexual, yellow or white flowers that could be male or female. Their female flowers have an inferior ovary and united style. They usually have branched tendrils, deeply cut leaves, and yellow flowers singly on the leaf axil.
Rind: The watermelon rind is hard, mid to dark green and usually mottled or striped.
Flesh: Watermelons have red to pink flesh with numerous black and white pips. Black pips are mature or fertile seeds, while white seeds are immature. The flesh is sweet and juicy in taste.
Nutrients: Watermelons are low in fat, containing 92% of water and 6% of sugar.
Cooking: Watermelon flesh can be eaten raw or used in preparations like smoothies, juices, salads, wraps, ketchup and many more dishes. You can also consume the fruit rind by making curry, pickles etc.
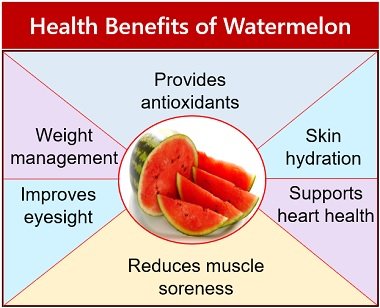
Watermelons have several health benefits, as mentioned in the image below:
Definition of Muskmelon
Muskmelons are succulents or edible fruits with hard, rough, netted rind and fleshy pulp with numerous pips at the centre. They belong to the gourd family (Cucurbitaceae), considered cucurbits or vine plants.
Watermelons are edible fruits cultivated in many tropical, subtropical and temperate regions. There are more than 825 species of muskmelons. Muskmelon vines are annual plants, having one growing season.
They are native to Iran, Anatolia and Armenia. Muskmelons are creeping plants whose fruit rests on the soil. You can see the physical traits of the muskmelon illustrated in the picture below.
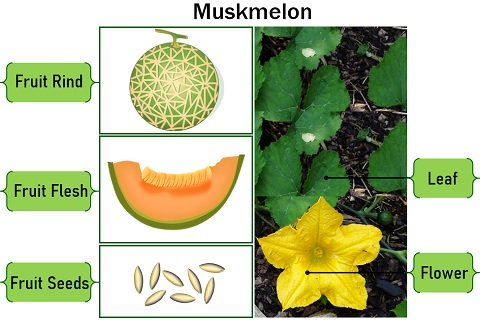
Vines: Muskmelon vines have unisexual, yellow flowers that could be male or female. Their female flowers have an inferior ovary and united style. They usually have clasping tendrils, round to lobed leaves and yellow flowers.
Rind: The muskmelon rind is generally hard, rough, netted and golden brown.
Flesh: Muskmelons generally have yellow to orange flesh with many beige-coloured pips in the central cavity. They have musky scented, sweet and juicy flesh.
Nutrients: Watermelons contain 90% of water, 9% of sugar and below 1% of protein and fat.
Cooking: The muskmelon pulp can be eaten raw or used in preparations like smoothies, juices, salads and many more. You can also fry and pickle the muskmelon rind.
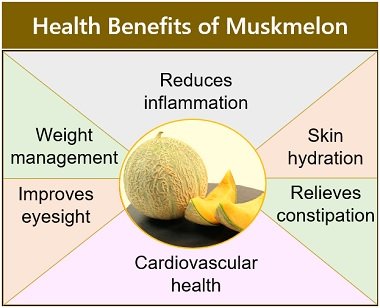
Muskmelons have various health benefits, as mentioned in the image below:
Key Differences Between Watermelon and Muskmelon
- Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) is a large, oblong fruit with hard, striped green skin and red pulp with many pips inside. While, Muskmelon (Cucumis melo) is a large, oval fruit with ribbed, netted or rough skin and yellow or orange pulp.
- Watermelons have a thick rind with green to dark green stripes on them. In contrast, muskmelons have comparatively thin with beige-coloured netted skin.
- Most muskmelons have peach-orange flesh with a soft and juicy texture and a sweet and musky aroma. Whereas most watermelons have pink to red coloured flesh with a dry or grainy texture and boast a triad of flavours like bitter, sweet, and sour.
- The watermelon seeds are black and sometimes white with a dispersed arrangement within the fruit. Oppositely, muskmelon seeds appear beige-coloured and are present in the central seed cavity of the fruit.
- The size of watermelons is comparatively large, as they usually weigh 3-4 kg with a diameter of 30-60 cm. On the contrary, muskmelons weigh 1.5-2 kg with a diameter of 10 cm.
Similarities
- Both watermelons and muskmelons belong to the Cucurbitaceae family.
- Watermelons and muskmelons are succulents having juicy and pulpy flesh.
- Cucurbits (Squash family) are the crop rotation group of both.
- Both need rich soil, plenty of compost, and a sunny location to grow.
- Watermelons and muskmelons are frost intolerant.
Conclusion
Watermelons and Muskmelons, even being from the same family, share different physical traits. Besides that, they taste great and offer excellent nutritional benefits during summer. The best thing they do is keep us hydrated on sunny days because they incorporate a large amount of water.