Hot air oven sterilization is a process of decontamination carried out by an electrical device that utilizes dry heat to sterilize various type of equipment or articles kept inside its chamber. It is used for sterilizing objects that cannot be subjected to wet sterilization and objects that are less prone to dry heat. It was initially developed by Louis Pasteur.
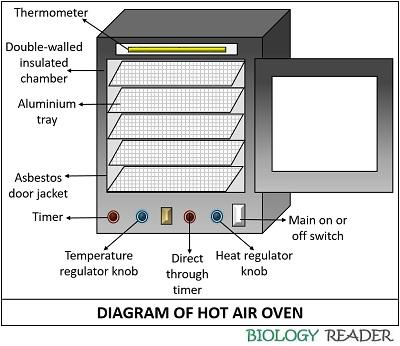
The hot air oven is operated within a temperature range of 50 to 300ºC by using the temperature regulator knob. It provides a continuous flow of heat through blowers or heaters and is equipped with a double-walled insulated jacket, perforated aluminium trays, main on/off switch, temperature regulator knob, and timer etc.
It also makes the use of biomarkers or temperature tapes to know whether the articles within the chamber are properly sterilized or not. In this context, we will discuss the construction, working, its types, advantages and disadvantages and various applications of the hot air oven.
Content: Hot Air Oven Sterilization
- Definition
- Construction
- Video
- Working
- Types
- Operation
- Maintenance
- Applications
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Conclusion
Definition of Hot Air Oven
A hot air oven is a type of dry heat sterilization that works on the principle of heat conduction, in which the articles are sterilized layer by layer, starting from the surface towards the centre. In this system, dry heat is recirculated within a chamber at a temperature ranging between 50-300 ºC to sterilize thermally stable objects. A hot air oven makes the use of dry heat to oxidize the cellular components of the microorganisms and their spores to kill them. A hot air oven is another way of sterilizing articles like glassware, metals, surgical equipment, powders etc. A diagram of a typical hot air oven is given below:
Construction of Hot Air Oven
A hot air oven consists of various parts that can be broadly classified under two heads viz. exterior components and interior components.
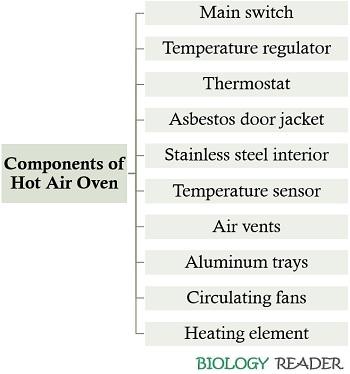
Exterior Components
- Main switch: It is used to switch on or switch off the instrument. A green indicator lights up when the device is switched on.
- Temperature regulator: It is used to regulate the temperature as per one’s requirement. The temperature increases when the knob is rotated to the right side and decreases when turned to the left.
- Thermostat: It is present at the top, whose one end is inside the oven. Its function is to check and maintain the desired temperature inside the hot air oven.
- Asbestos door jacket: This is the outer double-walled jacket, made of glass-wool fibre. Its primary function is to confine the heat generated within the chamber, thus conserving energy. It provides maximum thermal efficiency and also safeguards the instrument surfaces against heat damage.
Interior Components
- Inner chamber: It is made of stainless steel which supports long-lasting operation and also provides corrosion-resistant usage. On both sides, tray slots are found onto which the tray shelves can be adjusted or removed accordingly, considering the height and volume of the articles to be sterilized. The tray holder is made of stainless steel wire mesh cable.
- Temperature sensor: It senses the rise and fall in temperature inside the oven.
- Air vents: It is located towards the top of the chamber, which releases hot gases and excessive heat outside the oven.
- Aluminium trays: The articles like glassware, metals etc. are kept on the aluminium trays of the hot air oven. The trays are generally perforated to facilitate the equal distribution of heat to the articles that are kept inside.
- Circulating fans: It performs a central role in the uniform flow of heat inside the hot air oven along with the improved temperature distribution.
- Heating element: Electrical coils are placed at the bottom of the instrument, which allows the upward movement of heat.
Video
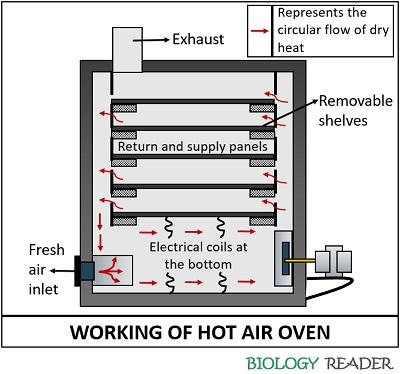
Working of Hot Air Oven
The working of a hot air oven is based on the principle of dry heat sterilization. It makes the use of hot air to kill the microorganisms or to sterilize various equipment. The heat generated within the chamber travels in such a manner that it first sterilizes the surface of the equipment and then the centre of them.
The hot air rises up to the top of the chamber and upon coming in contact with the surface of the chamber the air cools down and travels down. Therefore, the flow of hot air inside the oven is circular, which permits uniform heating and temperature distribution throughout the oven.
Considering that dry heat requires a different amount of time to sterilize different specimens, the following two factors should be kept in mind for carrying out sterilization, namely, thermal death point and thermal death time.
The thermal death point (TDP) is the lowest temperature required to kill all the microorganisms when applied for a specific time period. Thermal death time (TDT) is the minimum time taken to kill all the microorganisms at a specific temperature.
Different microorganisms will show different resistance towards heat, by which the TDP and TDT of microorganisms may vary depending upon the type of species. Endospore formers like Clostritridium botulinum are more heat resistant, while a few are less resistant towards heat. Dry heat kills the microorganisms by oxidizing or denaturing cellular components like protein.
Thus, while operating a dry heat sterilizer, we must consider the two factors like holding time of the microorganisms and optimum temperature to kill them. This table lists the standard settings for sterilization to kill different microbes.
| Temperature (in degrees) | Holding time (in minutes) |
|---|---|
| 180 | 20 |
| 170 | 40 |
| 160 | 60 |
| 150 | 150 |
Types
Hot air oven is generally available in two models, namely static and forced air type oven.
Static air-type oven: In this, the electric coils are located at the bottom, which permits the upward flow of the hot air. The movement of heat is through the gravity convection employing electrical coils at the bottom. Its efficiency is low in transferring heat energy.
Forced air-type oven: In this, the motor-driven blowers permits the uniform distribution of the hot air. The movement of heat is through forced or mechanical convection like air blowers. It is more efficient in heat conduction, i.e. it transfers the energy from the dry air more rapidly to the instrument.
Operation
The operation of the dry heat sterilizer typically involves the following steps.
- Firstly, plug in the oven and switch it on.
- Then, preheat the oven for at least 30 minutes before loading the items.
- After that, set the temperature gauge at the desired time relative to the volume of the contents that you need to sterilize.
- Load the articles on the middle shelf, or you can also put the remaining items on the other shelf depending upon the volume of articles.
- Maintain proper space between the equipment on the adjustable aluminium trays for adequate heat circulation.
Calibration: The calibration of the hot air oven is required to check the accuracy of the temperature necessary to kill the microbes. It should be done once a year. The calibration of the hot air oven involves the following steps:
- Firstly, connect the power cord.
- Then, keep the calibrated thermometer at the centre of the sterilizer.
- Then, switch on the device and set the temperature that you require.
- Check the thermometer every 15 minutes, until the desired temperature has been reached.
Maintenance
Like every device, a hot air oven also needs to be maintained to keep it in a proper working condition. For its maintenance, we need to follow the given measures.
- Clean the device once a week using wipes, paper towels etc.
- The oven should be operated on proper power, to avoid reduced performance and damage to the equipment.
- Place the hot air oven in such a place where the airflow around the blower motor is not restricted. Doing so ensures proper airflow inside the oven.
Safety Measures: Along with the maintenance of the device, we also need to consider a few safety measures that are given below:
- Glasswares should be thoroughly dried before placing it in the oven and wrapped in paper.
- Avoid using materials that are prone to heat damage.
- Do not place combustible items inside the oven.
- While operating the dry heat sterilizer, one should wear heat resistant gloves.
- Overcrowding the oven should be avoided.
Applications
Hot air oven performs a variety of functions in different fields like:

- It has baking, curing, drying and annealing applications as it efficiently removes the moisture content.
- Used to sterilizes heat-stable glass objects like flasks, pipettes, Petri-plates and test tubes, etc.
- Also used for sterilizing metal items such as scissors, forceps, spatula and scalpel, etc.
- Used to sterilize non-volatile compounds like sulphonamide, zinc and starch powder, etc.
- Widely used in research-based operations in the field of life science.
Advantages
- It is easy to operate, unlike an autoclave steam sterilizer.
- These are generally available in small sizes, which takes minimal space and is easy to install.
- It is non-corrosive for the metal equipment.
- It efficiently sterilizes heat stable and non-aqueous materials.
Disadvantages
- Dry heat sterilization has a significant drawback that it cannot kill the heat resistant endospores and microbial agents like prions.
- The heat penetration capacity and the killing of microorganisms is relatively slow in comparison to moist heat sterilization.
- Dry heat is not suitable for all types of equipment.
Conclusion
Therefore, we can conclude that the hot air oven functions as an insulated chamber that confines the electrically generated heat to dry and sterilize the specimen kept inside. It utilizes dry heat to remove moisture content from the equipment and sterilize heat-stable objects by killing microbial agents or microbial spores.