Phototropism in plants is a process where a plant bends in response to sunlight or any other light source. Plants sense light stimuli through their photoreceptors proteins. These specialized protein molecules or photoreceptors form a complex with the light-absorbing pigment (chromophore). When a chromophore absorbs light radiations, it brings changes in the photoreceptors’ structural configuration and initiates a signalling pathway. The signal then receives a light stimulus and responds accordingly.
We all know that the plants are the living organisms that remain fixed at one place by their roots. Thus, the plants cannot move, but they actually do. Now, you must wonder how the plants move? So, the answer is that the plants cannot walk like us, but their parts like the shoot system and root system tend to respond to external stimuli like light, water, wind, and chemical sources called tropism. Tropism merely refers to the response of living organisms, either similar or opposite to the direction of the external stimulus.
Phototropism merely refers to the plant’s directional movement (either towards or away) in response to a light stimulus. The plants mediate activities like energy production (photosynthesis), plant growth, and hormone production after receiving light stimuli. Some parts of plants (stems, leaves and flowers) show positive phototropism (bends towards the light). Oppositely, roots show negative phototropism (moves away from the light source).
In this context, definition, discoveries that led to the introduction of phototropism theory, mechanism, types and a brief overview of the phototropism phenomena. You will also get to know the role of plant hormones (phototropins and auxins) in the process of phototropism.
Content: Phototropism in Plants
- Definition of Phototropism
- History of Phototropism
- Mechanism of Phototropism in Plants
- Types of Phototropism
- Overview of Phototropism in Plants
- Role of Phototropins and Auxins in Phototropism
Definition of Phototropism
Photo means “Light” and tropism means “Turning”. Therefore, phototropism purely refers to the bending of the plant towards the light. Tropism can be defined as the growth of a plant towards any of the environmental stimuli like heat, light, air, water, chemicals and many other sources. The shoot system’s growth relative to the direction of the light stimuli is called phototropism or positive phototropic reaction. Oppositely, the root system’s growth is opposite to the path of the light stimuli is known as negative phototropism or geotropism.
Phototropism is a mechanism that is necessary for the survival of the plant. Thus, it is the “Survival mechanism” where the plant absorbs as much light. The more plant leaves will open towards the light, more will be the efficiency of the photosynthesis, which in turn allow more energy to generate.
History of Phototropism
Many scientists contributed to introduce different experiments, approaches, and opinions that have led to the discovery of the phototropism mechanism.
| Year | Discoverer | Discovery |
|---|---|---|
| 371-287 BC | Theophrastus | Discovered that the phototropism was due to removal of fluid from the illuminated site of the plants stem |
| 1561-1626 | Franscis Bacon | He discovered that phototropism was due to wilting |
| 1630-1684 | Robert Sharrock | According to him, plants get bends, due to fresh air |
| 1628-1705 | John Ray | According to him, plants bends towards the cool temperature when placed near the window |
| 1809-1882 | Charles Darwin | Hypothesized that one substance is produced at the tip of the plant which is responsible for the curvature of plant |
| 1926 | Nikolai Cholodny and Frit’s Went | They found high level of that substance that moved to the shaded side of the plant stem |
| 1904-1977 | Kenneth Thimann | Isolated and identified substance like “Auxin” |
Mechanism of Phototropism in Plants
The phototropism works on the principle of the light reaction. In phototropism, the photoreceptors in plants accept a light wavelength of around 450 nm and trigger a response. Blue light photoreceptor protein forms a complex, called phototropins. In the presence of light, auxin moves to the darker side of the stem.
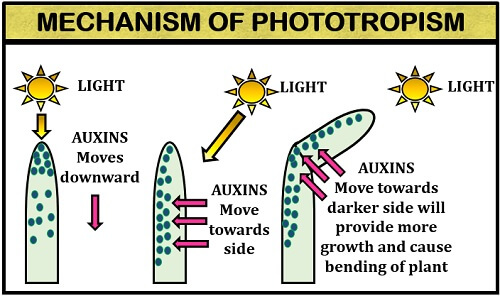
Auxin releases hydrogen ions in the plant cell and shifts towards the darker portion of the stem, leading to a decrease in the plant cell’s pH. The decrease in pH activates the release of an enzyme (expansins). The enzyme expansins will cause swelling in the cell and finally result in the plant’s bending towards the light.
Types of Phototropism
There are two types of phototropism that occurs in the plant, namely positive and negative phototropism.
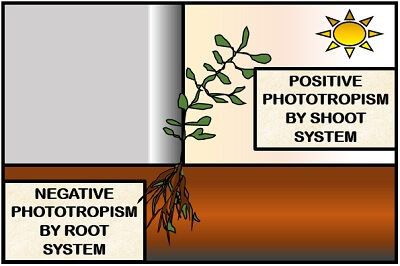
- Positive Phototropism: The movement or bending of plant parts (shoot system) in response to light, is the phenomena termed positive phototropism.
- Negative Phototropism: The movement or bending of plant part (root system) in response to light, is the phenomena termed negative phototropism.
Overview of Phototropism in Plants
Let us take a quick overview of the phototropism process by taking an example. We must have seen the bending of plantlets placed near a window towards the light. It is because plants need the exposure of sunlight to produce energy and food. The roots under the pot grow upward, and once they break through the surface, the shoot system starts bending towards the light.
The whole phenomena of bending of the plant can be understood by the signalling pathway concept that is explained below. Plant senses light, by the specific molecules called “Photoreceptors”. The photoreceptors are the protein molecules, which link with the chromophore pigment. Chromophore absorbs light and distorts the configuration and activity of the protein.
These alternations bring a signal in response to light, and the plants respond to promote gene expression, growth and hormone production. The pathway of the response production is called “Signalling pathway”. Therefore, phototropism is a directional response where a plant bends towards the stimulus (light).
Role of Phototropins and Auxins in Phototropism
The Phototropins are the photoreceptors, which detect the light and absorb the blue range of the spectrum. The plant’s tip (coleoptile) possesses a high concentration of auxin (plant growth hormone). An exposure of coleoptile to the sunlight causes an unequal distribution of phototropins.
Pht 1 and 2 are the two common types of phototropins in the higher plants, which respond differently towards the blue light. Under the influence of low-intensity blue light, phot-1 comes into action. In contrast, under the influence of high-intensity blue light, both phot 1 and 2 act redundantly.
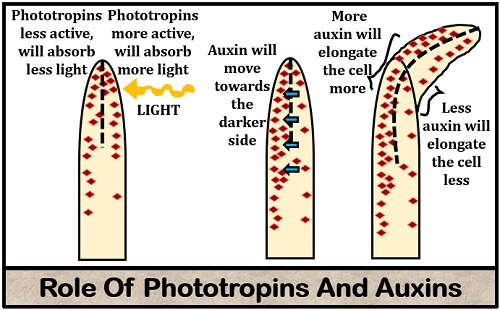
The primary functions of phototropins include stomatal opening, photosynthetic exchange, chloroplast movement, leaf-blade and cotyledon expansion. The phototropins will be more active or absorb more light in the lighter regions. Oppositely, the phototropins will be less active on the darker side or absorb less light.
Thus, an unequal transport of a plant hormone (auxin) towards the darker side of the coleoptile is due to the different level of phototropins. Auxin will shift more towards the darker side than the illuminated side. The auxin on the darker side of the stem will promote cell elongation and more growth, which results in bending of the plant in response to a light source.
Thank you