Riboflavin or Vitamin B-2 belongs to the Vitamin-B group, which are of eight kinds viz. vitamin B-1, B-2, B-3, B-5, B-6, B-7, B-9, B-12. It plays a crucial role in converting and breaking down protein, fats, and carbohydrates to produce energy. Vitamin B-2 converts complex carbohydrates, proteins and fat into simple sugar, amino acids and fatty acids, respectively by producing an energy molecule ATP (an energy currency of the cells to function).
Vitamin B-2 is one of the most important dietary supplement that our body needs. Spinach, fish, almonds, mushrooms, fortified grains, eggs, cheese etc. are rich in vitamin-B2. A person with vitamin B-2 deficiency should necessarily intake foods rich in vitamin B-2 as it cures migraines, neonatal jaundice, anaemia etc. You will get to know the definition, functions, degradation, deficiency, dosage, sources, side effects, and uses of the riboflavin in this context.
Content: Riboflavin
- Definition of Riboflavin
- Functions
- Degradation
- Riboflavin Deficiency
- Dosage and Sources
- Side Effects
- Uses of Riboflavin
Definition of Riboflavin
Riboflavin is an aromatic hetero-polycyclic organic compound, which belongs to the class “Flavin”, and it is a type of vitamin-B complex. Thus, it merely refers to the organic compounds that are composed of flavoproteins, and it belongs to the group of the water-soluble vitamin-B complex. Vitamin B-2 is a common name of riboflavin, which aids in cell growth and function. The alloxazine tricyclic ring is present in the structural moiety of vitamin B-2, which we could see in the image below.
Discovery: Vitamin B-2 was discovered in 1920, by Richard Kuhn and Theodor Wagner Jauregg. Then, in 1933, riboflavin was first isolated by Kuhn and Paul Gyorgy. The synthesis of riboflavin had started in the year 1935 by Paul Gyorgy. In the essential medicines, given by the world health organisation, riboflavin is the most effective medicine required for healthy living.
Let us look into some of the important properties of vitamin B-2:
| Properties | Riboflavin |
|---|---|
| Alternative / Common name | Vitamin B-2 |
| Chemical formula | C17H20N4O6 |
| Colour | Yellow |
| Half life | 66-84 minutes |
| Sensitivity | Sensitive to UV light and high temperature |
| Sources of Riboflavin: | |
| Avocado, squash, cherries etc. |
| Green leafy vegetables, kelp, mushrooms, tomatoes, asparagus etc. |
| Yogurt, milk and cheese |
| Meat, eggs and fish |
| Fortified cereals and nuts |
Functions
The functions of riboflavin include:
- Riboflavin acts as an important element in the formation of co-enzymes like FMN (Flavin mononucleotide) and FAD (Flavin adenine dinucleotide) by the assistance of an enzyme “Riboflavin kinase”.
- It provides energy to the cells by breaking down the nutrients present in the food, which we intake.
- Riboflavin helps in the metabolism of carbohydrate, protein and fats etc.
- Vitamin B-2 maintains the homocysteine to an average level in our body.
- Vitamin B-2 also protects tissue from lipid peroxidation.
- Riboflavin prevents acne and keeps the skin healthy by increasing the mucus secretion.
Degradation
Under UV exposure, the riboflavin degrades into various photo products. The photoproducts include formylmethylflavin (FMF), lumichrome (LC), lumiflavin (LF), carboxymethyl Flavin (CMF), 2,3- butanedione, β-keto acid and diketo compound. FMF acts as an intermediate product in the photodegradation of riboflavin.
Riboflavin Deficiency
Deficiency of Riboflavin is a clinical condition commonly known as “Ariboflavinosis”. The deficiency of riboflavin is not very common in western countries. The symptoms of vitamin B-2 deficiency include:
- Anaemia, fatigue, sore throat, low metabolism, cracked lips, mood swings, skin inflammation etc.
The symptoms appear just after a few days, according to the Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Riboflavin deficiency occurs by the two factors:
- A poor diet of vitamin B-2 is the primary factor.
- Poor absorption of vitamin B-2 and rapid excretion from the body is the secondary factor.
Dosage and Sources
Riboflavin is an essential dietary supplement. Its sufficient intake is necessary for our body. According to Oregon State University, the RDA (Recommended Daily Allowance) provides a reference amount of riboflavin per day, which is given in the table:
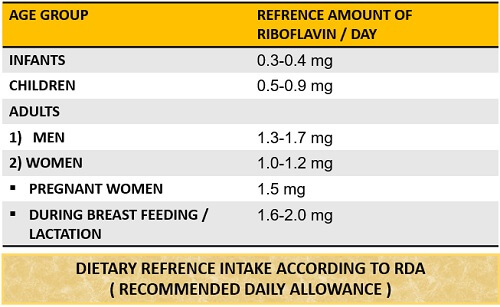
In terms of Estimated Average Requirements (EARs), riboflavin intake for men and women ages 14 are up to 1.1 mg and 0.9 mg per day, respectively. Thus, RDA and EARs provide an estimated uptake of vitamin B-2, and it collectively refers to as “Dietary Reference Intakes”.
The top five foods rich in vitamin B-2 are beef liver, yoghurt, milk, spinach, and almonds containing 3mg, 0.6mg, 0.4mg, 0.4mg and 0.3 mg, respectively. Therefore, people with vitamin B-2 deficiency must add vitamin B-2 rich foods to their diet.

Side Effects
According to the University of Maryland Medical Centre (UMM), excessive intake of vitamin B-2 can cause the following side effects:
- Itching
- Numbness
- Yellow or dark yellow urine
- Sensitivity towards light
- Burning or prickling
To maintain the level of vitamin B-2, a physician prescribes to take vitamin-B complex, in which vitamin B-2 is given in combination with other vitamin-B molecules.
Uses of Riboflavin
Riboflavin has the following benefits:

Helps in treating Migraine
High dose of up to 400mg/day is recommended for a person who experiences severe migraine attacks. Vitamin B-2 reduces the pain and frequency of the migraine. Nowadays, vitamin B-2 is used in combination with magnesium and coenzyme Q10 as a remedy or to manage migraine symptoms.
Promotes Healthy Skin and Hair
Vitamin B-2 maintains the level of collagen in our body, necessary to live young with healthy skin and hairs. Its deficiency can make you look aged. Vitamin B-2 also reduce the slow signs of ageing, skin inflammation etc.
Maintains an Eye Health
Deficiency of Vitamin B-2 can cause eye impairment like glaucoma. Glaucoma is an eye disease, in which a person loses his or her eyesight. In addition to glaucoma, eye cataracts, keratoconus etc. are also common in case of riboflavin deficiency. Vitamin B-2 maintains eye health, as the application of riboflavin drops to the surface of the cornea helps in treating the eye damage. Vitamin B-2 penetrates through the cornea and increases eye strength.
Rich in Antioxidants
Vitamin B-2 is rich in antioxidants, which controls the presence of free radical within our body. Vitamin B-2 secretes glutathione, which is an antioxidant that detoxes the liver.
Treats Cancer
Riboflavin also prevents certain types of cancer like colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, cervical cancer etc. It minimizes the effects of carcinogens and the presence of free radicals.
Regulates Energy
Vitamin B-2 produce energy in the form of ATP due to carbohydrate, protein and fat breakdown. Thus, vitamin B-2 converts nutrients of food into energy that a body can utilize. In simple words, vitamin B-2 maintains the metabolism of our body.
Treats Anaemia
Anaemia is a clinical condition that results in decreased production of RBCs. Vitamin B-2 helps in the steroid and RBCs synthesis. Thus, Vitamin B-2 aids in treating anaemia, which includes symptoms like fatigue, shortness of breath etc. Along with anaemia, vitamin B-2 also controls the level of homocysteine in the blood.
Hormonal Activity
Vitamin B-2 regulates thyroid and adrenal activity. Along with this, vitamin B-2 also helps in the recovery of chronic stress.
Treats Neurological Disease
Recent studies have shown that vitamin B-2 can also minimize the consequences of neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis etc.
Promotes Heart Health
Vitamin B-2 promotes heart health by maintaining the average level of homocysteine in the blood. A high amount of homocysteine in the blood can cause damage to arteries, blood vessels and increases the blood clotting, which sometimes leads to heart disease.
Therefore, people with high homocysteine should eat as much as fruits and green leafy vegetables, rich in vitamin B content. Hence, vitamin B-2 prevents heart disease, as it acts as an antioxidant that reduces the oxidative stress or removes free radicals from the body.