The difference between budding and grafting is mainly due to factors like:
- Scion (a detached living portion of the plant)
- Classification
In budding, a scion is a bud of the closely related plant is inserted into the rootstock of the original plant. In contrast, in the grafting method, a scion is a stem of a closely related plant is inserted into the shoot system of the original plant. Grafting is a method of vegetative propagation, while budding is one of the forms of grafting.
In this context, you will get to know the key differences between budding and grafting, along with the comparison chart. We will also discuss the definition, types and similarities.
Content: Budding Vs Grafting
Comparison Chart
| Properties | Budding | Grafting |
|---|---|---|
| Insertion | In this, bud of a plant is inserted into the rootstock | In this, stem of a plant is inserted into the rootstock |
| Evolution | Newly emerging technique | Ancient method |
| Scion | Bud | Stem |
| Expertise in handling | Requires less expertise | Requires technical skills |
| Size of the scion | Small | Larger |
| Period | Done during the period of growing season of the stock | Done during the period when the stock is dormant in the winter and early spring |
| Types | T, Inverted T, Patch, I, Forkert, Ring budding etc. | Cleft, Bark, Splice, Whip, Side Veneer, Saddle budding etc. |
| Application | Applicable for the fruit, nut and ornamental trees | Used to increase the quality of fruits, flowers or leaves |
Definition of Budding
It is defined as the horticulture method of vegetative propagation of a bud. In budding, a bud is cut off with some bark into and inserted into another rootstock by many ways. Budding is a type of grafting, where a scion is a bud instead of a stem. It is widely used in the vegetative propagation of ornamental trees and fruits (peach, plums, apple etc.) and commonly employed during the active growing season.
Definition of Grafting
It is defined as the horticulture method of vegetative propagation of a stem. In grafting, a stem is cut off in such a way that another stem can insert. Both the stems then unite and grow as an individual plant. It is widely used in the vegetative propagation of flowering plants and fruits (peach, plums, apple etc.) and commonly employed during the dormant season (winter and early spring).
Types of Budding
There are several methods in the process of budding, which includes:
T-method: In this method, the bud is inserted into the T-shaped insertion in the original plant’s rootstock.

Inverted T budding: In this method, the horizontal cut is made at the bottom, and the vertical cut is applied on the top. Therefore, the insertion is the contrast to the T budding.

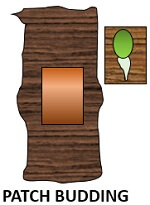
Patch budding: In this patch of a bud is inserted into the rectangular patch of the bark removed from the rootstock.
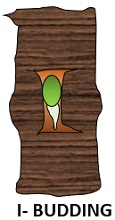
I budding: In this method, a rectangular bud patch is inserted into the rootstock’s I-shaped insertion.
Forkert budding: In this method, the scion is inserted into the rootstock of the shape (∏). Then this forkert patch is pulled downwards to insert the bud.

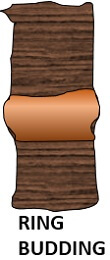
Ring budding: This method is also called annular budding. A complete circle is an incision over the stem’s rootstock where the bud stick is then inserted in this method.
Types of Grafting
There are several methods in the process of budding, which includes:
Cleft graft: In this, the stem is inserted into the V-shaped rootstock.

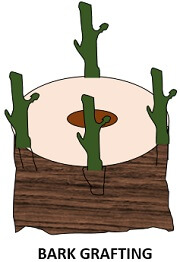
Bark graft: In this, the stem is inserted into the flap cuts in the cambium of the root system.
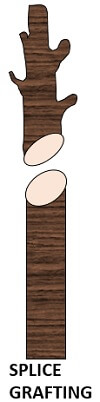
Splice graft: In this, a diagonal cut is made on both the stem and rootstock so that they can overlap each other.
Whip graft: It is also called tongue graft. In this, an insertion is made so that both stem and the rootstocks have interlocking tongues.

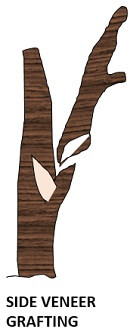
Side veneer grafting: In this, the stem is inserted into the removed wedge of the rootstock.
Saddle graft: In this, both the scion and the rootstock is cultured into the V-shape.

Key Differences Between Budding and Grafting
- A plant’s bud is inserted into the second plant in budding, whereas a plant’s stem is inserted into another plant in grafting.
- Budding is the newly emerging technique, while grafting is the ancient method.
- Bud is the scion in budding, whereas stem is the scion in grafting.
- Budding is a method that requires less expertise in comparison to the method of grafting.
- The budding process is done during the growing season of the stock, whereas grafting is done during the period of dormant condition (in the winter and early spring).
- Budding is a method practised for the vegetative propagation of the fruits, nuts and ornamental trees, whereas grafting is adapted to increase the quality of fruit, flowers or leaves.
Similarities
- Both budding and grafting are horticulture techniques.
- The plants used for the scion into another rootstock is of closely related species.
- The process is the same, as the scion is inserted into the rootstock and develop into a composed plant.
- The rootstock after insertion gives a healthy plant tolerant to drought, disease etc.
Conclusion
In grafting, the leaves, flowers and seeds are produced by the scion of the plant that has been inserted into another rootstock. The nutrient is supplied through the rootstock of the original plant, where the scion is inserted. In budding, the bud is cut out with some bark, and the bark is in direct contact with the rootstock of the growing plant.