The difference between light reaction and the dark reaction is mainly due to the following properties:
The demand for light: A light reaction demands a source of light energy for breaking down water into oxygen, while a dark reaction does not need a light source.
Site of occurrence: A light reaction occurs within the thylakoid membrane, whereas a dark reaction occurs inside the aqueous stroma of the chloroplast.
Light and dark reaction are the two phases that complete the process of photosynthesis in photosynthetic organisms. This post describes the key differences between the light and dark reaction, along with the comparison chart and definition of the two.
Content: Light Reaction Vs Dark Reaction
Comparison Chart
| Properties | Light reaction | Dark reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It involves the conversion of light energy from sunlight into cellular energy (ATP and NADPH), by the oxidation of water molecule | It involves the conversion of cellular energy (ATP and NADPH) into chemical energy or sugars, by the reduction of carbon dioxide |
| Alternative names | Light dependent or Hill’s reaction | Light independent or Blackman’s reaction |
| Phase of photosynthesis | It is the first phase of photosynthesis and also refers as “Photochemical phase” | It is the second phase of photosynthesis and also refers as “Biosynthetic phase” |
| Light requirement | It strongly requires the presence of light source | It occurs in absence of light source |
| Site of occurrence | Occurs in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplast | Occurs in the stroma of chloroplast |
| Functional role | It liberates oxygen by splitting water | It fixes carbon dioxide to produce sugar |
| Photolysis | Occurs in photosystem-II | Does not occur |
| End product | Its end product is oxygen with a release of ATP and NADPH | Its end product is sugar with a release of ADP and NADP |
| Involvement of chlorophyll | It involves the presence of photosynthetic pigment or chlorophyll to absorb the light energy | It lacks such pigment |
Definition of Light Reaction
It is the first phase of photosynthesis, where a plant derives cellular energy, i.e. ATP and NADPH, from the light energy, i.e. sunlight. The photochemical phase or light reaction is a stage that involves the oxidation of a single water molecule into half oxygen molecule.
Therefore, the splitting of two water molecules will result in releasing one oxygen molecule. Oxidation of water releases ATP and NADPH, which provides cellular energy to the plant cells to prepare food for themselves.
It occurs during the daytime or in the presence of sunlight. For the reconstruction of light energy, a light reaction includes two photosystems, namely PS-I and PS-II.
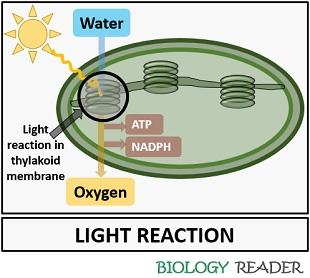
PS-I harnesses a light wavelength of 700 nm, while PS-II harnesses a light wavelength of 680 nm. The site of light reaction is within the thylakoid membrane of the photosynthetic apparatus (Chloroplast). It generally involves the following steps:
- Absorption of light energy coming from sunlight.
- Hydrolysis of a water molecule
- Release of oxygen into the atmosphere
- Formation of cellular energy, i.e. ATP and NADPH
Definition of Dark Reaction
It is the second phase of photosynthesis, where a plant exploits the cellular energy (ATP and NADPH) released from the light reaction to produce chemical energy by synthesizing sugars.
The biosynthetic phase reduces six CO2 molecules and twelve H2 molecules from the NADPH into a single glucose (C6H12O6) molecule.
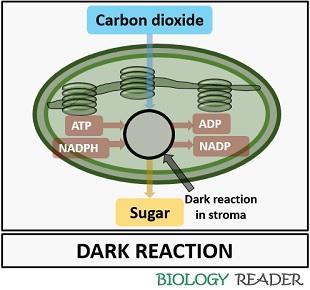
The hydrolysis of ATP and NADPH releases ADP and NADP. It occurs in the absence of sunlight. A location of the light-independent reaction is inside the aqueous stroma of the photosynthetic apparatus (Chloroplast). It generally involves the following steps:
- Usage of chemical energy coming from the light reaction.
- Fixation of carbon dioxide
- Formation of glucose
- Release of ADP and NADP
Key Differences Between Light Reaction and Dark Reaction
- A light reaction involves the conversion of light energy from sunlight into cellular energy (ATP and NADPH) by the oxidation of water molecule. A dark reaction transforms cellular energy (ATP and NADPH) into chemical energy or sugars by reducing carbon dioxide.
- The alternative names for the light reaction are light-dependent or Hill’s reaction, while alternative names for the dark reaction are light-independent or Blackman’s reaction.
- A light reaction strongly requires the light source to produce cellular energy for the plants, whereas a dark reaction occurs in the absence of light.
- Light reaction plays a functional role in liberating oxygen by splitting water, whereas dark reaction plays a fundamental role in fixing carbon dioxide to form glucose.
- The light reaction involves photosynthetic pigment, i.e. chlorophyll, to trap the light energy in the thylakoid membrane. The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast, which lacks the chlorophyll pigments.
Conclusion
Therefore, we can conclude that both photochemical and biosynthetic phase share many differences, but they collectively accomplish the process of photosynthesis. They follow a cyclic pathway, where both the light and chemical energy are continuously used and released.
Thank you for the information.