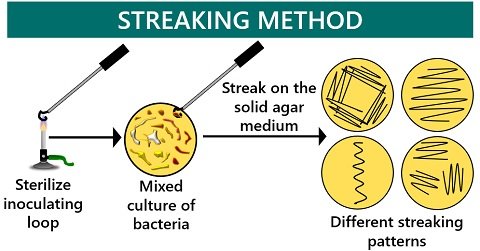
The quadrant streaking method is one of the streaking methods extensively used to obtain a pure culture. It helps to isolate a single colony or single species from the mixed culture. Streaking involves various patterns like a quadrant, continuous and radiant.
In the quadrant streaking method, a little inoculum is deposited on the first quadrant of an agar plate and successively spread over the remaining three quadrants. Separate microbial colonies mainly form on the third and fourth quadrants.
The isolated colony can be further cultured in the selective growth medium to know the growth pattern and cultural characteristics of the desired microorganisms. You can also perform the IMViC test (Indole test, Methyl red test, Voges Proskauer test and citrate utilization test) and other biochemical tests to classify the organism further.
This post describes the definition of the streak plate method. You will also get to know the meaning, objective, principle, procedure, advantages, limitations and significance of the quadrant streaking method.
Content: Quadrant Streaking Method
- Streak Plate Method Definition
- Quadrant Streaking Method Meaning
- Objective
- Principle
- Procedure
- Precautions
- Advantages
- Limitations
- Significance
Streak Plate Method Definition
It refers to the pure culture technique that involves inoculating the separated colony from the mixed culture (either broth culture or directly from the culture plate/slant) over the solid agar surface by moving the sterilized inoculating loop back and forth. Loeffler and Gaffkey introduced the streaking method. The streaking method is a dilution technique that dilutes the inoculum via successive streakings on the solid agar. Thus, it significantly produces individual or discrete colonies.
Quadrant Streaking Method Meaning
It is the common streaking method of isolating individual cells by preparing areas of dilution or quadrants. The colonies become thinner or isolated colony forms due to successive dilution of the inoculum by streaking the growth plate over four times. The individual microbial species grow and multiply to form a discrete colony or colony-forming unit. Quadrant streaking is a four-phase streaking method.
Objective
The quadrant streaking method involves the following two objectives:
- It dilutes the microbial sample or inoculum on the surface of the agar medium by successive streaking until bacteria spread well enough to produce isolated colonies.
- It produces discrete colony-forming units on the agar surface. Other plating methods (like pouring and spreading) may cause overcrowding of microbial colonies, making the isolation and enumeration difficult.
Principle
The quadrant streaking method’s principle involves inoculation of a little inoculum on successive quadrants of the solid agar surface. The number of organisms in the inoculum decreases by sequential streaking. Eventually, the inoculum is diluted to a point where a single bacterial cell growth occurs after every few millimetres on the agar surface. It uses a sterilized inoculating loop, swap or toothpick to make striations over the solid culture medium.
Procedure of Quadrant Streaking Method
It basically involves the sterilization of all equipment, media preparation and inoculation of inoculum in the four successive quadrants by using a sterile inoculating loop each time.
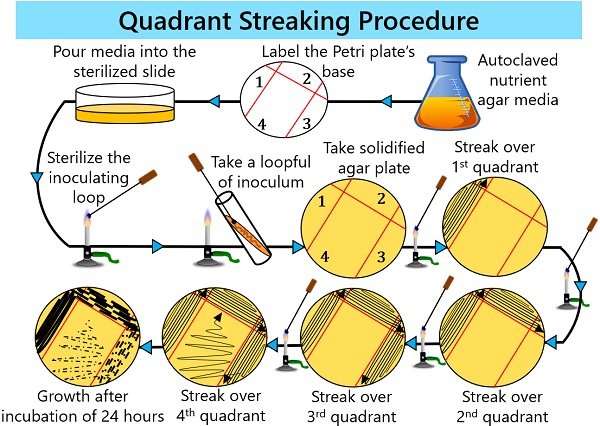
- First, prepare nutrient agar media as per the requirement. Then, autoclave the freshly prepared nutrient agar media at 121 degrees Celsius for 20 minutes.
- Then, keep the NAM and others materials like culture plate, inoculating loop, marker and sterilized Petri plates inside the laminar air flow chamber.
- Label four quadrants on the backside of the Petri plate in a way shown in the diagram. Then, pour the molten nutrient agar media into the Petri plate and allow it to solidify.
- Sterilize the inoculating loop over the blue flame until it becomes red hot or free from any microorganisms.
- Then, take a loopful of inoculum from the original sample (either the bacterial slant or culture plate) near the burning flame.
- Afterwards, gently streak the inoculum in the first quadrant of the solid agar media by moving the inoculating loop in a zig-zag pattern. After that, cover the lid of the Petri plate and sterilize the inoculating loop over the blue flame to kill the remaining microbes.
- Then, lightly drag the inoculating back and forth on the second quadrant by intersecting the streaks of the first quadrant only two or three times. Instantly cover the lid of the Petri plate to avoid any contamination.
- Again, sterilize the loop and striate the inoculum from the beginning of the second streak to the third quadrant. Cover the lid of the Petri plate.
- Then, sterilize the loop and perform the fourth streak by intersecting streaks of the third quadrant, extending up to the middle of the plate. Before keeping the inoculating loop aside, sterilize it for the last time.
- Invert the streaked plate and label the plate’s base with your name, date and other details.
- Finally, incubate the plate within the incubator at a desired temperature and time.
Precautions
Some preventive measures should be considered while performing the experiment:
- First, you should sterilize all the equipment.
- It would be best to label the culture plate before streaking to avoid the unwanted mess.
- The agar media must be appropriately solidified, or it must be free of condensed moisture.
- To streak the solid agar surface, only take a small quantity of inoculum.
- Avoid gouging the agar plate while inoculating the microorganism.
Advantages
- The quadrant streaking method enables us to work with an individual or well-isolated colonies.
- It is a rapid isolation method.
- It sequentially dilutes the population size of the microorganism in the original sample.
- Quadrant streaking separates organisms from mixed cultures.
- The inoculating loop is sterilized between streaks to reduce the number of microorganisms (mainly bacteria).
- Microscopic examination becomes easy.
Limitations
- The concentration of the sample is unknown.
- It requires a person with good streaking skills.
- Constant sterilization of inoculating loop is required to produce separate colonies.
Significance
The quadrant streaking method is significantly used to separate a pure strain from the mixed population. We could examine cultural characteristics of the organism like colour, texture, size, and other microscopic and macroscopic properties by performing the quadrant streaking method. By adding antibiotics to the growth media, the sensitivity and resistance of the inoculated organism can be known.